Malaria pathogen under the X-ray microscope
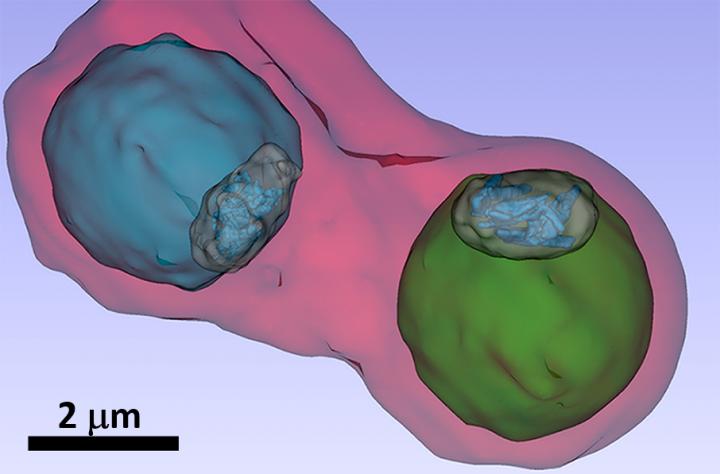
The image shows details such as the vacuole of the parasites (colored in blue and green) inside an infected blood cell. Credit: S. Kapishnikov
The main avenue to deal with the disease is treatment by active compounds in the quinoline family and, more recently, from the artemisinin family. However, the exact way that active compounds keep the pathogenic plasmodia in check has so far been subject to controversy.
One thesis relates to the digestive process of the pathogenic plasmodia. Research has shown that plasmodia store large amounts of hemoglobin in their digestive vacuole, an organelle that resembles a bag.
This releases iron-containing hemozoin molecules that the plasmodia cannot tolerate. The plasmodia manage to crystallize these toxic hemozoin molecules so that they can no longer poison them. The idea was that active compounds might prevent the formation of hemozoin crystals and thus boycott the detoxification process of the plasmodia.
A team led by Sergey Kapishnikov from the University of Copenhagen and the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel, together with Danish, Spanish, French and Berlin colleagues, has now investigated this process in infected blood cells for the first time.
The blood cells were infected with the malaria pathogen Plasmodium falciparum and then mixed with different concentrations of bromoquine from the quinoline family.
Malaria pathogens in blood cells can only be examined in vivo and in their natural environment using X-ray microscopy at synchrotron sources. Other investigation methods, such as electron microscopy, require the pathogens to be dried and cut into ultra-thin slices.
At BESSY II, Stephan Werner and Peter Guttmann together with Sergey Kapishnikov were able to examine the samples using X-ray microscopy. “The blood samples are flash-frozen for the examination so that we can observe the pathogens in vivo and also produce three-dimensional X-ray tomography images”, explains Guttmann. Further X-ray microscopy studies were carried out at the ALBA synchrotron light source in Barcelona.
Fluorescence spectromicroscopy at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility ESRF in Grenoble made it possible to map the distribution of elements in blood cells . When combined with the cellular structure revealed by the three-dimensional X-ray images, the bromoquine distribution and its mode of action could be precisely interpreted.
“We see in our images that the bromoquine accumulates at the surface of hemozoin crystals. This should lead to inhibition of the crystal growth and thus disrupt the detoxification process by the plasmodia parasites”, explains Kapishnikov.
These investigations can also be extended to other drug groups such as Artemisinin and provide valuable information for the design of more effective malaria treatments.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



