Megakaryocytes act as „bouncers“ restraining cell migration in the bone marrow
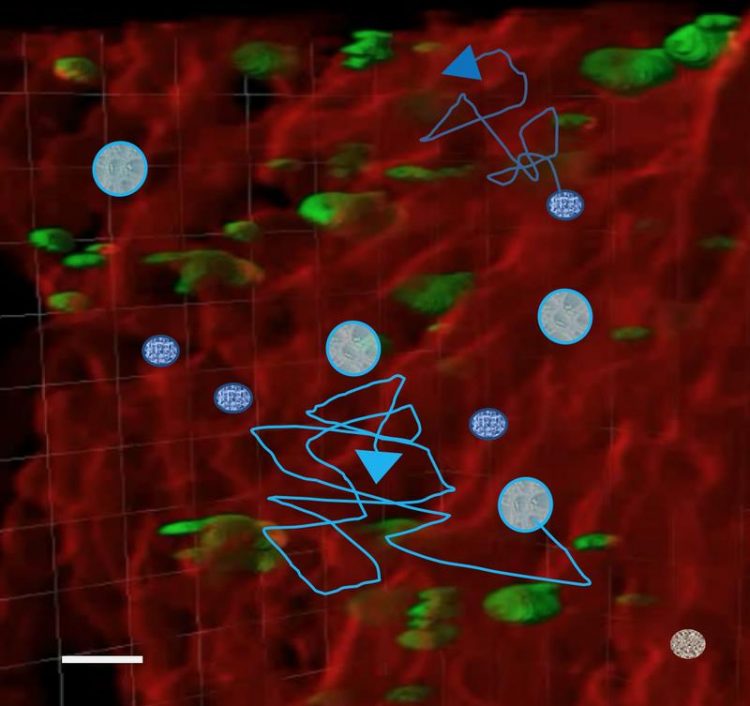
Fig1: Illustration of the concept using 3D fluorescence images as bio. templates for cell migration simulations (red: vessels, green: megacaryocytes, blue: Hemapoietic stem cells, cyan: Neutrophils Rudolf-Virchow-Zentrum, Uni Würzburg
Hematopoiesis is the process of forming blood cells, which occurs predominantly in the bone marrow. The bone marrow produces all types of blood cells: red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells (leucocytes).
One of the most prominent white blood cell types are neutrophils – they help the body fight against infections and are the most abundant subpopulation of leukocytes. They are short-lived and highly mobile, and can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot.
All hematopoietic cells that develop in the bone marrow must cross the blood vessel wall to enter the circulation system. Blood platelets are released by bigger vessel-penetrating protrusions of huge, largely immobile progenitor cells, named megakaryocytes.
In this way mature megakaryocytes produce platelets and release them into the blood circulation to maintain constant platelet counts. In addition, they actively regulate hematopoietic stem cell accumulation in a positive as well as negative manner.
Imaging the entire bone marrow with subcellular resolution to understand how all the players act in concert is still challenging. The research groups of Prof. Katrin Heinze and Dr. David Stegner established a profound 3D image reconstruction and segmentation pipeline for different bone marrow components.
These segmented objects, originally derived from Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy, then serve as templates (see Figure 1) for computational simulations of cell distributions and their migration behavior in the bone marrow.
Megakaryocytes influence cell migration significantly
In this study, the scientists found that hematopoietic stem cells and neutrophils migration depends on the megakaryocyte size and distributions. Thus, these simulations suggest that megakaryocytes play an important role in cell migration even if not migrating themselves.
Instead, the large megakaryocytes represent passive obstacles, and thus significantly influence migration of other cells such as hematopoietic stem cells and neutrophils in the bone marrow. Indeed, intravital microscopy confirmed that neutrophil mobility was reduced in platelet-depleted mice where megakaryocyte volumes are increased (see Figure 2).
This study showcases how the combination of advanced imaging approaches in combination with computational simulations can sharpen this hypothesis. Heinze says, “For simulations, grids and spheres do not sufficiently represent the complexity of the vasculature and its cells. In contrast, our image-derived templates are suitable and thus highly superior, as they reflect the physiological architecture in the bone very well.”
“This study points to the importance of biomechanical properties of the bone marrow environment in regulating cell motility, a factor which has so far not been appreciated well. Our data clearly show that volumetric analysis of the number and localization of megakaryocytes provides additional information that sharpens our picture of the bone marrow dynamics and mechanisms,” Stegner explains.
The computational tool can not only support 3D studies of dynamic cell behavior, but also help to focus or reduce animal experiments when hypotheses can be tested computationally. Beyond bone and blood research, the method can be used for any organ or tissue to interrogate dynamic maps of selected cell types and structures in health and disease.
Funding
This work is funded by the TRR-SFB240 and the Rudolf Virchow Center for Experimental Biomedicine at the University of Würzburg.
Dr. Daniela Diefenbacher (Press Office, Rudolf Virchow Center, University of Würzburg)
Tel. 0931 3188631, daniela.diefenbacher@uni-wuerzburg.de
Prof. Dr. Katrin Heinze has been head of a research group at the Rudolf Virchow Center for Experimental Biomedicine at the University of Würzburg since 2011. Since 2017 she is University Professor of Molecular Microscopy.
Tel. +49 (0)931 31 84214, katrin.heinze@virchow.uni-wuerzburg.de
Dr. David Stegner is a group leader at the Institute of Experimental Biomedicine – Chair I. He utilizes advanced imaging modalities to understand the role of platelets in thrombo-inflammation.
Tel. +49 (0)931 31-80419, stegner@virchow.uni-wuerzburg.de
Gorelashvili MG, Angay O, Hemmen K, Klaus V, Stegner D, Heinze KG. Megakaryocyte volume modulates bone marrow niche properties and cell migration dynamics. Haematologica. 2019 Jun 27. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.202010. [Epub ahead of print]
https://www.uni-wuerzburg.de/en/rvz/rvz-news/single/news/megakaryocytes-act-as-b…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Durable, Efficient, Sustainable: The Rise of Cerium Oxide Thermal Switches
Groundbreaking cerium oxide-based thermal switches achieve remarkable performance, transforming heat flow control with sustainable and efficient technology. Cerium Oxide-Based Thermal Switches Revolutionize Heat Flow Control Thermal switches, which electrically control…

How Industrial Robots are Reducing Emissions in Global Manufacturing
A new study explores the intersection of industrial automation and environmental sustainability, focusing on the role of industrial robots in reducing the carbon intensity of manufacturing exports. The research demonstrates…

Patients Can Heal Through Precise, Personalized Bioceramic Grafts
A recent review is transforming the landscape of craniomaxillofacial bone regeneration with the introduction of personalized bioceramic grafts. This pioneering research explores the fabrication and clinical potential of synthetic grafts…



