
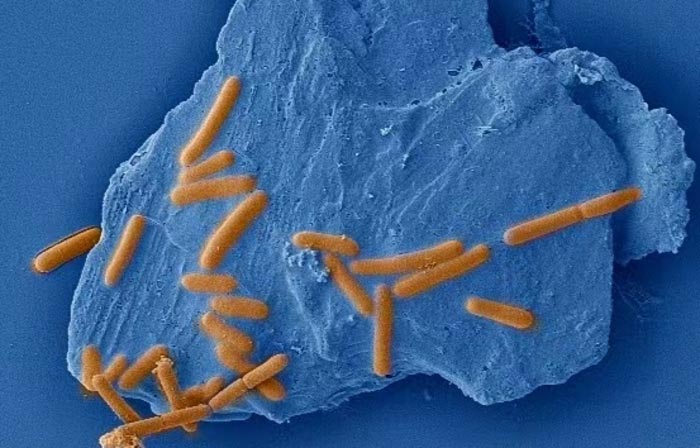
An anaerobic, motile, gram-positive bacterium adheres to the molybdenite (MoS2) surface to uptake the trace elements from the mineral structure for cell synthesis.
Credit: ©Science China Press
… play important roles in geological and environmental processes.
Minerals are the fundamental components of Earth. Microbes occupy the majority of the tree of life. In near surficial environments, minerals and microbes co-exist and interact. The studies of mineral-microbe interactions have blossomed in the last two decades, because such interactions drive major geological events and substantially determine the habitability of the Earth. A research team led by Dr. Hailiang Dong from China University of Geosciences (Beijing) has critically reviewed the mineral-microbe interactions and their coevolution, and proposed major research opportunities and challenges in the future.
Minerals and microbes mutually interact across all spatial and temporal scales. While many minerals offer protection and supply nutrients/energy to support microbial growth and metabolism, other minerals may release bio-toxic substances and produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) to limit and even to kill microorganisms. In return, microbes actively dissolve, precipitate, and transform minerals through metabolism, which may produce special biosignatures in geological record.
Throughout Earth history, both minerals and microbes increase their species diversity and functional complexity. In a prebiotic world, minerals catalyze synthesis of biological molecules and play an essential role in life emergence. Subsequently, mineral evolution drives microbial innovation through their changes of physiochemical properties through time. Microbial evolution in turn drives mineral diversification through their unique metabolism. Therefore, the evolving mineral-microbe interactions over geological time play critical roles in driving geological events such as occurrence of the Great Oxidation Event and the formation of large ore deposits.
Mineral-microbe interactions have many biotechnological applications including bioleaching of precious metals and manufacturing of mineral fertilizers, remediation of heavy metal and organic pollutants, biosynthesis of novel materials and CO2 sequestration. Despite recent advances, the authors identify major research questions for future research.
First, the roles of minerals in supporting microbial ecology are only qualitatively recognized at present. Traditional culture media do not consider minerals as important nutrients and energy, which may be one of the reasons for a low success rate of obtaining pure cultures. Mineral-based culture media should recover more microbial resources.
Second, it is challenging to distinguish biogenic minerals from abiogenic ones. A syngenetic assemblage of minerals that combine morphological, structural/textural, and geochemical evidence is more meaningful to search for the biological footprints in geological record and on other planets.
Third, it is imperative to link laboratory mechanistic investigations to field observations. Through an iterative approach mineral-microbe interactions may be inferred through time.
Fourth, manipulation of mineral-microbe interactions can benefit the humankind, such as CO2 sequestration and mitigation of the global warming effect, resource recovery, environmental protection, and manufacturing of novel materials.
See the article:
National Science Review
A critical review of mineral-microbe interaction and coevolution: mechanisms and applications.














