Near-infrared probe decodes telomere dynamics
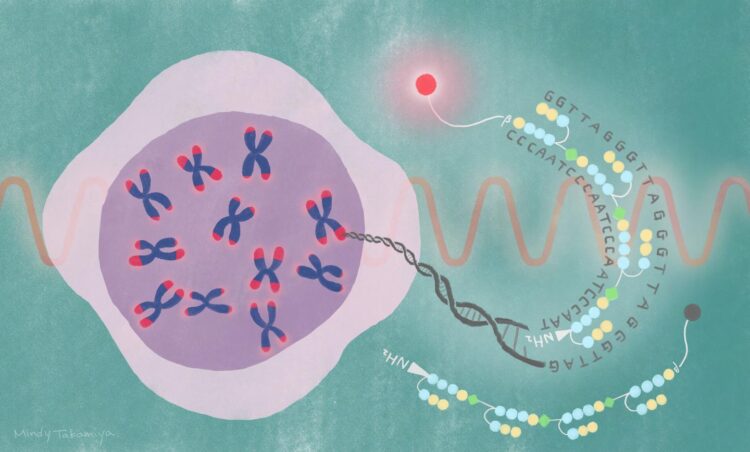
A fluorescent compound was attached to the PIP that targets the DNA repeating sequence found in telomeres. This probe, called SiR-TTet59B, enables observation of telomeres in action.
Credit: Mindy Takamiya/Kyoto University iCeMS
A repetitive DNA sequence that causes health risks when it malfunctions can now be watched inside living cells using a synthetic tool.
A new synthetic probe offers a safe and straightforward approach for visualizing chromosome tips in living cells. The probe was designed by scientists at the Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Science (iCeMS) and colleagues at Kyoto University, and could advance research into aging and a wide range of diseases, including cancers. The details were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
“Chromosome ends are constantly at risk of degradation and fusion, so they are protected by structures called telomeres, which are made of long repeating DNA sequences and bound proteins,” says iCeMS chemical biologist Hiroshi Sugiyama, who led the study. “If telomeres malfunction, they are unable to maintain chromosome stability, which can lead to diseases such as cancer. Also, telomeres normally shorten with each cell division until they reach their limit, causing cell death.”
Visualizing telomeres, especially their physical arrangements in real-time, is important for understanding their relevance to disease and aging. Several visualization approaches already exist, but they have disadvantages. For example, some can only observe telomeres in preserved, or ‘fixed’, cells. Others are time-consuming or involve harsh treatments that denature DNA.
Sugiyama and his colleagues overcame these issues by using a synthetic pyrrole-imidazole polyamide (PIP) probe that can precisely deliver a fluorescent compound to telomeres on the tips of chromosomes.
“PIPs are a class of small molecules made from pyrrole and imidazole molecules that can be pre-programmed to bind to a selected DNA sequence,” explains Yutaro Tsubono, the first author of this study.
The team designed a PIP that targets the DNA repeating sequence found in telomeres. A fluorescent compound, called silicon-rhodamine, was attached to the PIP. The probe, called SiR-TTet59B, binds to telomeres in living cells. When the low-intensity near-infrared light is shone on the cells, the silicon-rhodamine fluoresces, showing the telomeres in action.
“Our study on this programmable, near-infrared probe creates opportunities to use these molecules in biological and medical applications,” says iCeMS bioengineer Ganesh Pandian Namasivayam.
The team used their probe to observe telomere dynamics during different phases of cell division and to gauge telomere length by measuring the fluorescence intensity. Being able to visualize telomere length was both surprising and exciting, says Namasivayam, as it can be developed to create an efficient and robust approach for detecting severe telomere shortening in diseases, such as age-related retinal degeneration, with low energy light.
Since PIPs can be designed to target any DNA sequence in the genome by changing their arrangement, the scientists anticipate the approach can be adapted to make near-infrared fluorescent probes for visualizing other important DNA sequences related to disease.
###
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.0c04955
About Kyoto University’s Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS):
At iCeMS, our mission is to explore the secrets of life by creating compounds to control cells, and further down the road to create life-inspired materials.
https:/
For more information, contact:
I. Mindy Takamiya/Mari Toyama
pe@mail2.adm.kyoto-u.ac.jp
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Parallel Paths: Understanding Malaria Resistance in Chimpanzees and Humans
The closest relatives of humans adapt genetically to habitats and infections Survival of the Fittest: Genetic Adaptations Uncovered in Chimpanzees Görlitz, 10.01.2025. Chimpanzees have genetic adaptations that help them survive…

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…



