New Disease Gene for Early Infantile Epilepsy found
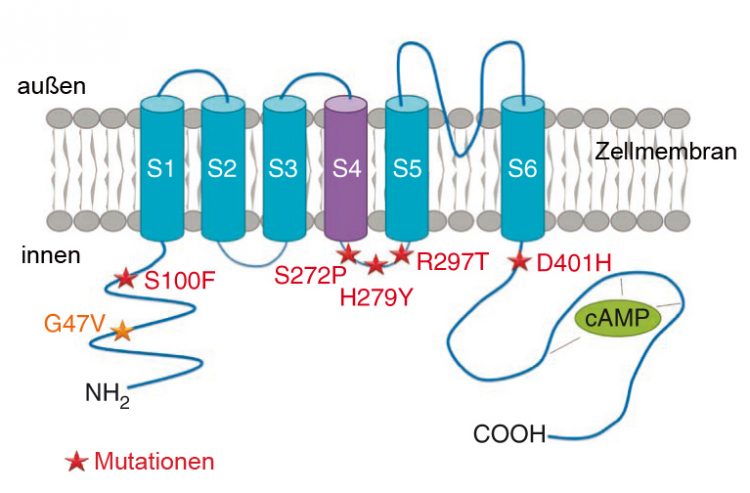
Structure of the HCN1 channel in the cell membrane of nerve cells. The asterisks mark the spots where mutations were found that cause an early infantile epilepsy resembling the Dravet syndrome. Picture: Institute for Human Genetics
Epileptic encephalopathies are severe disorders which occur even in babies. They are accompanied by a disturbed maturation of the brain as well as by an impairment of the mental and sometimes also of the motoric development. Seizures typically appear first in combination with fever and cannot usually be treated.
Another form of early infantile epileptic encephalopathy, which has been known for some time, is the Dravet syndrome. It occurs in about one child out of 30,000 and is caused by mutations of the sodium channel gene SCN1A. However, many children suffering from a disorder resembling the Dravet syndrome have no mutations of SCNA1, so there must be other genes responsible for this early infantile type of epilepsy.
Mutations discovered in the HCN1 ion channel
In the search for new disease genes as the cause of early infantile epileptic encephalopathies, scientists from Paris and Würzburg have now made a discovery. In the genetic material of nearly 200 affected children, where mutations of the SCNA1 gene had already been ruled out, they discovered in six cases the pathogenic mutations in another ion channel gene, namely HCN1. These dominant mutations arise spontaneously during the generation of the parents' reproductive cells; they are not present in the parents' body cells.
“The electric current carried by the HCN1 cation channel is also referred to as 'pacemaker', because it stimulates rhythmic activity in spontaneously active nerve cells”, says Professor Thomas Haaf, head of the Institute for Human Genetics of the University of Würzburg Animal models had already suggested that this channel has a key role in epileptic disorders. “But so far no corresponding mutations had been found in patients.”
Differences from the Dravet syndrome
At the beginning the seizures of children with mutations of the HCN1 gene are hardly distinguishable from the Dravet syndrome, but at later stages they are: “There is an increased occurrence of atypical seizures. All affected children have an impairment of intelligence and behavioural disorders, including autistic behaviour”, says Professor Haaf.
The study was led by Dr. Christel Depienne, who worked for two years until the end of 2013 as a visiting scientist at the Würzburg Institute for Human Genetics. From there she coordinated the German-French research team.
Consequences of the new discovery
How can patients benefit from the new findings? This is not an easy question to answer, because it is usually a long way from the discovery of a pathogenic gene mutation to the therapy.
Professor Haaf comments: “In any case, a better understanding of the molecular causes of the disorder will be helpful in the development of new therapeutic approaches, for example of drugs with a specific effect on the HCN1 currents. The results enable us already to make a correct diagnosis of this very severe early infantile disorder, which usually occurs sporadically, and to provide genetic counselling to parents with regard to their further family planning.”
“De novo mutations in HCN1 cause early infantile epileptic encephalopathy”, C. Nava, C. Dalle, A. Rastetter, …, T. Haaf, E. Leguern, C. Depienne, Nature Genetics, published online on 20 April 2014, doi:10.1038/ng.2952
Contact
Prof. Dr. Thomas Haaf, Institute for Human Genetics of the University of Würzburg, T (0931) 31-88738, thomas.haaf@uni-wuerzburg.de
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-wuerzburg.deAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



