New horizons for organoboron and organosilicon chemistry
Credit: Tokyo Tech
…with triple elementalization.
In recent years, organic chemicals containing boron (B) and silicon (Si) have found applications in various fields, including optoelectronics and pharmaceuticals. Moreover, they can also serve as building blocks for complex organic chemicals. As a result, scientists are actively looking for new ways to leverage these versatile chemical tools as well as produce more kinds of organosilicon and organoboron compounds.
One limitation of the synthesis methods currently available for these chemicals is that we cannot introduce multiple B- and Si-containing groups in aromatic nitrogen heterocycles, i.e., carbon rings in which one of the carbon atoms is replaced by a nitrogen atom. If we could produce and freely transform such molecules, it would unlock the synthesis of several compounds relevant in medicinal chemistry.
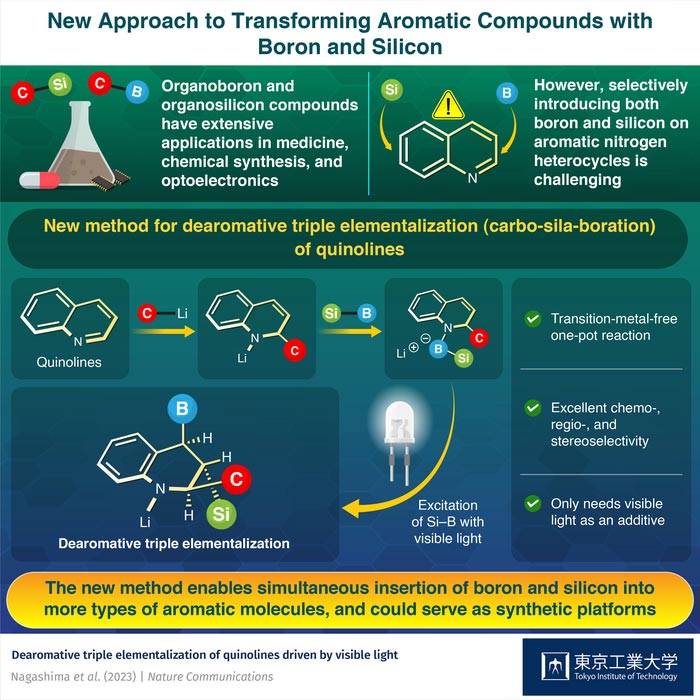
Fortunately, a research team including Assistant Professor Yuki Nagashima from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), Japan found a straightforward way around this limitation. As explained in their most recent study published in Nature Communications, the team developed a method that allows them to modify quinolines, small organic molecules with an aromatic nitrogen heterocycle, with B-, Si-, and carbon-containing groups simultaneously.
Their approach begins with a quinoline or a quinoline derivative that reacts with an organolithium compound with the desired carbon group. This carbon group attaches itself at one of the carbon sites of the nitrogen heterocycle. Then, a single compound containing the Si and B groups joined by an Si–B bond is introduced. This compound replaces the lithium atom and attaches itself through the B group at the nitrogen site.
Finally, by stimulating and eventually breaking the Si–B bond with blue light, the B and Si groups reorganize in a predictable fashion, attaching themselves at different locations within the nitrogen heterocycle. This, in turn, yields a triple hetero-elementalized (carbo-sila-boration) quinoline derivative as the final product.
The team tested their synthesis approach to produce over 30 quinoline derivatives, some of which were produced in high yields. Most notably, the proposed method provided excellent stereo-, chemo-, and regio-selectivity, meaning that the reaction produced the desired compound with high specificity. To top it off, the process was “one-pot” and required only visible light as the additive, greatly reducing the associated costs and time.
Through various experiments and detailed computational analysis, the team further revealed the mechanism at play behind their approach. “Based on our calculations and experimental results, we conclude that the on-site generation of silyl radical species, rather than silyl anions, upon light irradiation facilitates the overall triple hetero-elementalization reaction,” explains Dr. Nagashima. The insight will surely prove important for future chemists seeking to develop new synthesis methodologies based on this technique.
Finally, as a proof-of-concept, the team tested a particular hetero-elementalized quinoline as a scaffold for the synthesis of organic compounds. Put simply, they tested how easily one could replace the Si and B groups with arbitrary functional groups, such as -OH, methyl, and phenyl groups. The results were promising, as Dr. Nagashima highlights with eyes on the future: “Although chemo- and stereoselective transformations of Si–B groups are still under study, we believe the carbo-sila-borated quinolines could become versatile synthesis platforms.”
Let us see what interesting applications organic chemists can find for the method showcased by the Tokyo Tech team!
Journal: Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36161-4
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: Dearomative triple elementalization of quinolines driven by visible light
Article Publication Date: 6-Feb-2023
Media Contact
Reiko Hattori
Tokyo Institute of Technology
hattori.r.ac@m.titech.ac.jp
Office: +81-3-57343794
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



