New insights into the world of trypanosomes
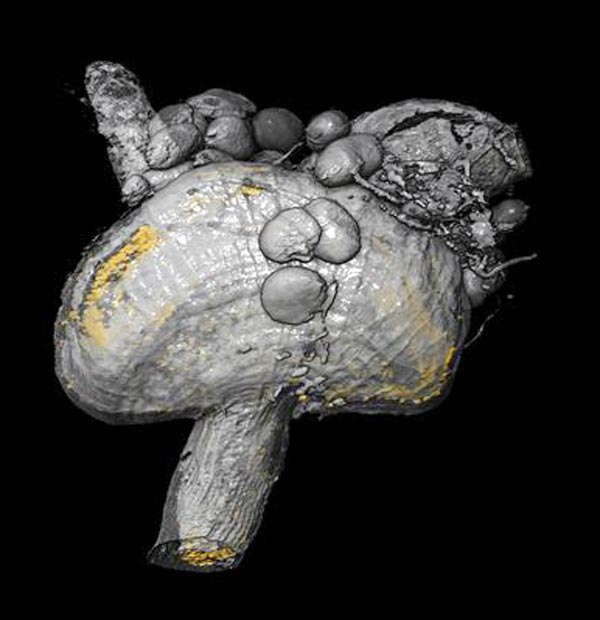
3D model of the proventriculus, a special organ of the tsetse fly: The distribution of the trypanosomes based on the fluorescent cell nuclei is shown in yellow. (Picture: Chair of Zoology I/eLife)
Single specimens of the vermicular pathogens causing sleeping sickness swim inside the gut of the tsetse fly between blood cells which the fly has ingested from an infected mammal.
This is where they start their week-long journey through the fly's internal organs. In other places, they have clustered together to form a teeming swarm so dense that nothing is visible of the fly's structures.
Trypanosomes are the pathogens responsible for sleeping sickness. Inside the fly's salivary gland, they attach to the epithelium in huge numbers while continuing to beat their flagella at high frequency. In this position, the parasites remain waiting until the tsetse fly bites a human or an animal to be released into the victim's blood stream with the saliva.
Habitats inside the fly where mapped three-dimensionally
A team of researchers from the Biocenter of Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany, has captured these and other processes in high-resolution pictures and videos. What is more, they used light sheet microscopy to map all habitats of the parasites inside the fly in 3D.
“These images are unparalleled,” Tim Krüger says. Thanks to the detailed images, the scientists are now able to take the surprisingly complex microenvironment of the trypanosomes into account when investigating the infectious disease in more detail. Krüger studies the parasites at the JMU’s Chair of Cell and Developmental Biology in the team of Professor Markus Engstler.
Lash-like protrusion serves as drive
Trypanosomes are protozoa that move with the help of flagella, which are lash-like appendages protruding from the cell. “They are highly dynamic and never stop the flagellar beating,” Krüger explains. “This enables them to swim and navigate effectively in various environments.” And the parasites are capable of doing so not only inside the fly, but also in the blood stream, in skin, fat tissue, the brain and other organs of humans and animals.
In a new publication in the journal eLife, the Würzburg team shows detailed 3D images of the trypanosomes' anatomy in all developmental stages inside the tsetse fly. They analysed the swimming behaviour in the different tissues and present among others imaging techniques that allow tracking and quantifying entire swarms of the pathogen inside the fly.
Swimming behaviour of the parasites inside the tsetse fly unclear
The JMU scientists want to use this new range of analysis options to examine the trypanosomes in more depth. Because it is still largely unclear how and on which ways the dangerous pathogens swim through the fly's body before infecting a human.
One strategy to combat sleeping sickness is to interrupt or prevent pathogen development already in the tsetse fly. “But this can only succeed if we know exactly how the trypanosomes behave inside the fly,” Tim Krüger says.
Exploring “microswimming” effects
Physicists also have an interest in the high-resolution images from the Biocenter. “Our cooperation partners have a keen interest in this, because they are dealing with so-called 'microswimmers',” as Krüger explains. To be more precise, they are interested in the hydrodynamic effects of swimming motions at small scales, at the individual cell level and in collective swimming phenomena. This is a complex topic since the effects here are completely different from those of larger objects swimming in water.
In turn, the team of Professor Engstler hopes to glean important stimuli from physics: “If we have a better understanding of the interactions between parasites and hosts also at the physical level, we can develop new approaches to explain how the parasites adapt and how the infectious processes inside the hosts evolve.”
Facts about sleeping sickness
Trypanosomes are wide-spread in sub-Saharan Africa. The protozoan parasites are transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly. Each year, there are around 30,000 new infections. Initial symptoms include headaches and joint pains followed by confusion, seizures and other symptoms in later stages. Finally, the sufferers fall into a coma and die.
There are no vaccines available against the pathogens; the available drugs can have extreme side effects. So there is urgent demand for better medication to treat the disease. Trypanosomes not only infect humans. They also kill cattle, goats and other livestock thereby causing enormous damage: In some regions of Africa, livestock breeding is hardly possible due to the trypanosomes.
Link to the online publication
eLife is a multidisciplinary open-access journal which covers life science topics. The Würzburg videos and animations on the behaviour of the trypanosomes in tsetse flies are incorporated in the journal article: https://elifesciences.org/articles/27656
Schuster, S., Krüger, T., Subota, I., Thusek, S., Rotureau, B., Beilhack, A., Engstler, M. (2017): Developmental adaptations of trypanosome motility to the tsetse fly host environments unravel a multifaceted in vivo microswimmer system. eLife, 15 August 2017, DOI: 10.7554/eLife.27656.001
Contact
Dr. Timothy Krüger, Chair of Zoology I (Cell and Developmental Biology), Biocenter, JMU, T +49 931 31-84277, tkrueger@biozentrum.uni-wuerzburg.de
http://www.zeb.biozentrum.uni-wuerzburg.de/ Website of the Chair of Zoology I, JMU
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-wuerzburg.deAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



