New method for removing oil from water
Silently and efficiently, the bionic oil collector removes contamination from a water surface. The adsorbing functional textiles were developed based on nature's example. (c) W. Barthlott, M. Mail/Uni Bonn
The video clip is as short as it is impressive: The 18-second sequence shows a pipette from which dark-colored crude oil drips into a glass of water. Then a researcher holds a green leaf against the spot.
Within a matter of seconds the leaf sucks the oil from the surface of the water, leaving not even a trace behind.
The star of the movie, the small green leaf, comes from the floating fern Salvinia. The special abilities of its leaves make it highly interesting for scientists, because they are extremely hydrophobic:
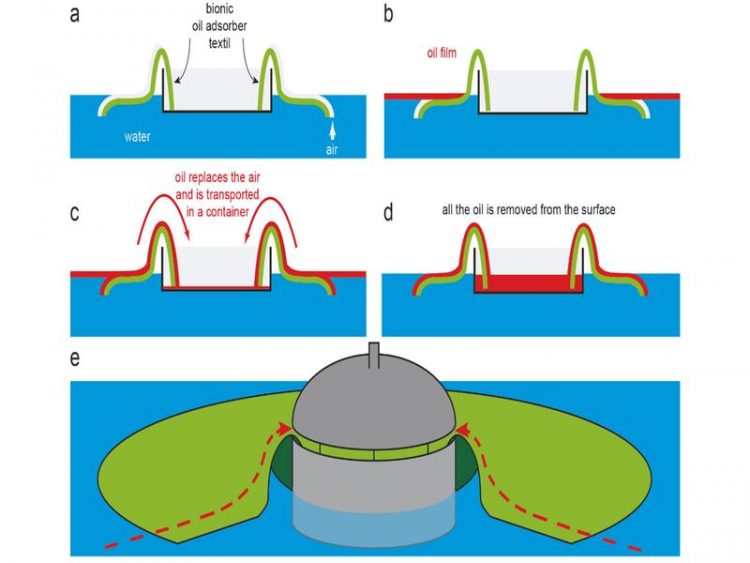
When submerged, they wrap themselves in an air jacket and remain completely dry. Researchers call this behavior “superhydrophobic”, which can be translated as “extremely water repellent”.
However, the Salvinia surface loves oil which is, in a way, a flip side of superhydrophobia. “This allows the leaves to transport an oil film on their surface”, explains Prof. Dr. Wilhelm Barthlott, emeritus of the University of Bonn and former director of its botanic gardens. “And we have also been able to transfer this property to technically producible surfaces, such as textiles.”
Functional textiles as “suction tubes”
Such superhydrophobic substances can then for instance be used to remove oil films from water surfaces efficiently and without the use of chemicals. However, unlike other materials that have been used for this purpose so far, they do not absorb the oil. “Instead, it travels along the surface of the fabric, moved forward solely by its adhesive forces,” explains Barthlott.
“For example, in the laboratory we hung such fabric tapes over the edge of a container floating on the water. Within a short time they had almost completely removed the oil from the water surface and transported it into the container.”
Gravity provides the power; the bottom of the container must therefore be below the water surface with the oil film. “The oil is then completely skimmed off – as if using an automatic skimming spoon for meat stock.”
This also makes super-hydrophobic textiles interesting for environmental technology. After all, they promise a new approach to solving the acute environmental problem of increasing oil spills on water bodies. Oil films floating on water cause a number of problems.
They prevent gas exchange through the surface and are also dangerous on contact for many plants and animals. As oil films also spread quickly over large surfaces, they can endanger entire ecosystems.
Cleaning without chemicals
The new process does not require the use of chemicals. Conventional binding agents simply absorb the oil and can then usually only be burned later. The superhydrophobia method is different: “The oil skimmed into the floating container is so clean that it can be reused,” explains Prof. Barthlott.
The procedure is not intended for large-scale oil disasters such as those that occur after a tanker accident. But particularly small contaminations, such as engine oil from cars or ships, heating oil or leaks, are a pressing problem. “Even minor quantities become a danger to the ecosystem, especially in stagnant or slow-flowing waters,” emphasizes the biologist. This is where he sees the major application potential of the new method, for which a patent has been filed by the University of Bonn.
Generally speaking, many surfaces exhibit superhydrophobic behavior, albeit to varying degrees. The basic prerequisite is first of all that the material itself is water-repellent, for example due to a wax coating. But that alone is not enough: “Superhydrophobia is always based on certain structures on the surface, such as small hairs or warts – often on a nanotechnological scale,” explains the botanist from the University of Bonn. It is also thanks to him that science now knows much more about these relationships than it did a few decades ago.
The research work is funded by the Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt DBU. “This now helps us to develop oil-absorbing materials with particularly good transport properties, in cooperation with RWTH Aachen University,” says Barthlott.
Prof. em. Dr. Wilhelm Barthlott
Nees-Institut für Biodiversität der Pflanzen
Universität Bonn
Tel. 0228/732271 (Secretary’s office)
E-mail: barthlott@uni-bonn.de
W. Barthlott, M. Moosmann, I. Noll, M. Akdere, J. Wagner, N. Roling, L. Koepchen-Thomä, M.A.K. Azad, K. Klopp, T. Gries & M. Mail (2020): Adsorption and superficial transport of oil on biological and bionic superhydrophobic surfaces: a novel technique for oil-water separation. Philosophical Transactions A., DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2019.0447
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-bonn.de/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

NASA: Mystery of life’s handedness deepens
The mystery of why life uses molecules with specific orientations has deepened with a NASA-funded discovery that RNA — a key molecule thought to have potentially held the instructions for…

What are the effects of historic lithium mining on water quality?
Study reveals low levels of common contaminants but high levels of other elements in waters associated with an abandoned lithium mine. Lithium ore and mining waste from a historic lithium…

Quantum-inspired design boosts efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion
Rice engineers take unconventional route to improving thermophotovoltaic systems. Researchers at Rice University have found a new way to improve a key element of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) systems, which convert heat…



