
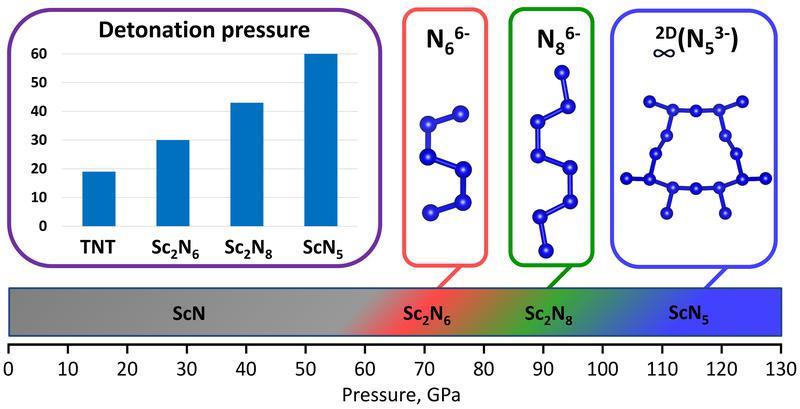
Detonation pressure of the synthesized high-pressure scandium polynitrides and their characteristic oligo- and poly-nitrogen structural units, accountable for the high-energy-density property of the compounds.
(c) UBT
Researchers at the University of Bayreuth have synthesized unique scandium polynitrides under extreme conditions, with exotic chemistry and potential applications as high-energy-density materials. Their results are published in the “Nature Communications” journal.
High-energy density materials (HEDMs) are pivotal in various applications due to their superior energetic performance, which includes high detonation velocity, detonation pressure, and energy storage capacity. Their application in space exploration as rocket propellants and in defense as explosives is of critical importance for modern society. The unique chemical properties of these materials, such as the ability to store vast amounts of energy in a relatively small volume, make them indispensable for advancing technology in areas requiring high-power outputs and compact energy storage solutions.
Nitrogen-bearing compounds are among the most effective choices for HEDMs. Nitrogen’s ability to form various stable and energetically favorable bonds of different order, single N-N, double N=N, or triple N≡N, allows for the synthesis of a wide range of compounds with tailored properties. Nitrogen-rich materials are capable of releasing a huge amount of energy during decomposition or combustion (when single bonds are replaced by triple ones), making them highly effective as propellants and explosives. The decomposition of nitrogen-bearing compounds often results in the formation of nitrogen gas (N2), which is a stable, inert, and environmentally friendly product.
For mastering HEDMs, the molecular weight is a very important parameter: the lighter the elements forming a solid, the higher the gravimetric energy density of the compound. Since scandium is the lightest transition metal, its polynitrides (compounds containing numerous single-bonded nitrogen atoms) are especially promising as HEDMs, as was predicted in many computational studies. However, hitherto scandium polynitrides have been unknown.
Researchers from the University of Bayreuth report on four novel scandium nitrides, Sc2N6, Sc2N8, ScN5, and Sc4N3. “The two novel catenated nitrogen units N66- and N86- obtained in this study, significantly expand the list of anionic nitrogen oligomers that make a remarkable contribution to the fundamental understanding of nitrogen chemistry under high pressure”, says PhD student Andrey Aslandukov, first author of the paper.
“Synthesized Sc2N6, Sc2N8, and ScN5 solids are promising high-energy-density materials with calculated volumetric energy density, detonation velocity, and detonation pressure up to 3 times higher than those of common explosives trinitrotoluene (TNT). High-pressure chemistry demonstrates the existence and diversity of polynitrides, opening perspectives for their applications in science and technology”, says Prof. Leonid Dubovinsky.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Prof. Dr. Dr. h.c. Leonid Dubrovinsky
Bavarian Research Institute of Experimental Geochemistry & Geophysics (BGI)
University of Bayreuth
Phone: +49 (0)921 / 55-3736 or -3707
E-mail: Leonid.Dubrovinsky@uni-bayreuth.de
Originalpublikation:
Aslandukov, A., Aslandukova, A., Laniel, D. et al. Stabilization of N6 and N8 anionic units and 2D polynitrogen layers in high-pressure scandium polynitrides. Nat Commun 15, 2244 (2024) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46313-9














