Obesity & Hypertension: Researchers Discover Novel Mechanisms
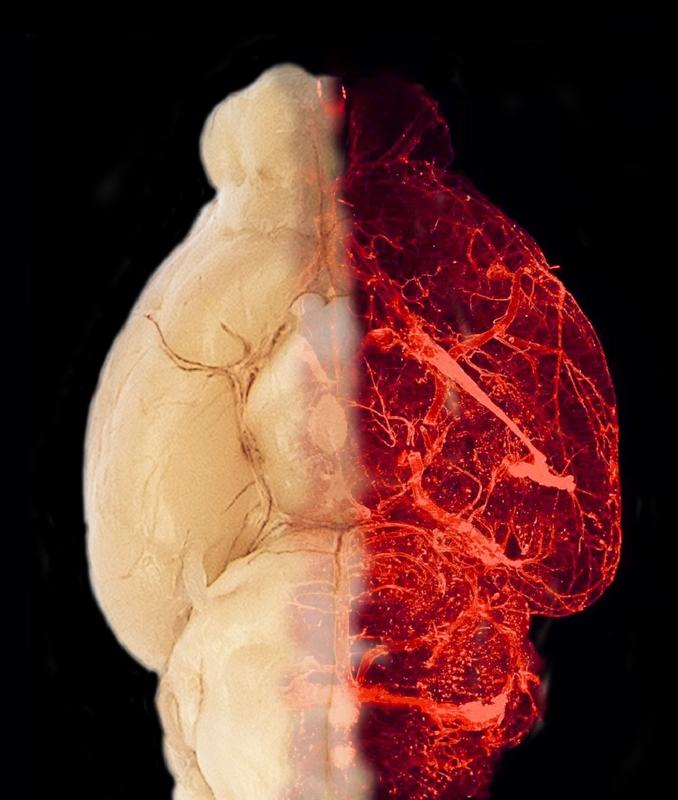
Blood vessels in the transparent brain of an obese mouse model ©Helmholtz Zentrum München; Tim Gruber
Researchers have succeeded for the first time in demonstrating the role of hypothalamic astrocytes in obesity-related hypertension. In addition, they showed that the hormone leptin is involved in the increase of blood vessels in the hypothalamus of obese mice, contributing of hypertension. Helmholtz Zentrum München led the study and collaborated with Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, the Technical University of Munich and the German Diabetes Center.
Hypertension is a widespread comorbidity of patients with obesity that greatly increases the risk of mortality and disability. In recent years, researchers have found that a high-calorie diet increases the density of blood vessels (hypervascularization) in the hypothalamus – an important “eating control” area in our brain. Researchers hypothesized that elevated hormone levels of leptin are associated with a higher risk of developing hypertension. However, the exact mechanisms that contribute to the condensed growth of blood vessels in the hypothalamus were unknown.
New research conducted by Cristina García-Cáceres’ research group at Helmholtz Zentrum München has now revealed that obese mice do not increase the amount of blood vessels in the hypothalamus when they lack the hormone leptin. Leptin is produced by adipose tissue, is involved in the control of hunger and satiety, and plays an important role in the regulation of fat metabolism in humans and mammals.
Once the researchers increased the hormone leptin in these mice, certain brain cells, the astrocytes, boosted the production of a specific growth factor. This growth factor, in turn, promoted vessel growth. The result was an increased number of vessels in the hypothalamus (and no other brain region). The scientists thus demonstrated that leptin is mainly responsible for the increased concentration of vessels in the hypothalamus and that this process is mediated via astrocytes.
“We provide a paradigm shift in our understanding of how the hypothalamus controls blood pressure in obesity,” explains first author Tim Gruber. “While previous research has focused primarily on neurons, our research highlights the new role of astrocytes, historically assumed less relevant than neurons, in controlling blood pressure”.
Looking into the future, according to study leader Cristina García-Cáceres, one important question remains: How exactly do astrocytes communicate with neurons? “We have started to answer this question using in vivo real-time imaging of astrocyte-neuron circuit function in the hypothalamus,” the researcher says.
Original Publication:
Gruber et al., 2021: Obesity-associated hyperleptinemia alters the gliovascular interface of the hypothalamus to promote hypertension. Nature Metabolism, DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.04.007
Highlight-Artikel in Nature Reviews Endocrinology: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41574-021-00511-3
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



