Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

Study describes new approach to treating AIDS-associated syndrome
Increasing the body’s production of growth hormone may be an effective treatment for HIV lipodystrophy, a syndrome involving the redistribution of fat and other metabolic changes in those receiving combination drug therapy for HIV infection. Researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) report that administration of growth-hormone-releasing hormone to a group of men with HIV lipodystrophy significantly improve
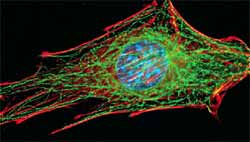
CNRS and Inserm research scientists at the Institut Curie have shed new light on the function of huntingtin, the protein whose mutation underlies Huntington ’s disease. This neurodegenerative disease,like Alzheimer ’s or Parkinson ’s,is characterized by the abnormal death of certain neurons.
The scientists have discovered that huntingtin,like a “booster rocket “,accelerates the transport of a neuron survival factor. When huntingtin is mutated, the “booster rocket ” malfunctions, transport

University of Toronto microbiologists have used pattern recognition software to discover the function of yeast genes essential to cell life – knowledge that could help scientists determine what causes cells to die, as well as what they need to live.
“Given the similarities between the yeast and human genomes, our work should promote advances in genomics research in both yeast and humans,” said Professor Timothy Hughes of U of T’s Department of Medical Genetics and Microbiology, who led the

Modern optical microscopes are high-tech devices with complex functions and operations. So that not just specialists can get the best out of these advanced instruments, Leica have produced a microscope which automatically selects the optimal combination of optical components.
Many modern items of equipment can do too much. It is not only when operating a video recorder or a mobile phone that you can quickly end up in the depths of some menu full of unclear functions. New features are overlo

Current microarray experiments allow the levels of activity of thousands of genes to be measured at once, providing a window into molecular events underlying health and disease. The selection of genes having distinct levels of activity between conditions of interest (such as cancer and non-cancer) has therefore emerged as a key aim of data analysis. However, with typically many thousands of genes to choose from and at most a few dozen sets of measurements available, differential analyses of this kind

The Centre for Stem Cell Biology (CSCB) at the University of Sheffield is welcoming some of the world’s leading experts to its International Human Embryonic Stem Cell Symposium on Friday 9 July 2004. The CSCB is a world-leading centre for stem cell research, and has produced two of the UK’s six embryonic stem cell lines. The symposium will allow around 200 scientists to benefit from the experience of the world’s leading researchers in this area.
Embryonic stem cell technology is a new are