
From seat cushions to mattresses to insulation, foam is everywhere — even if we don’t always see it. Now, researchers at The University of Texas at Dallas have fused chemistry with technology to create a 3D-printed foam that is more durable and more recyclable than the polymer foam found in many everyday products. The research, which appears in the March 1 print edition of RSC Applied Polymers, a journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry, focused on creating a sturdy but lightweight foam…
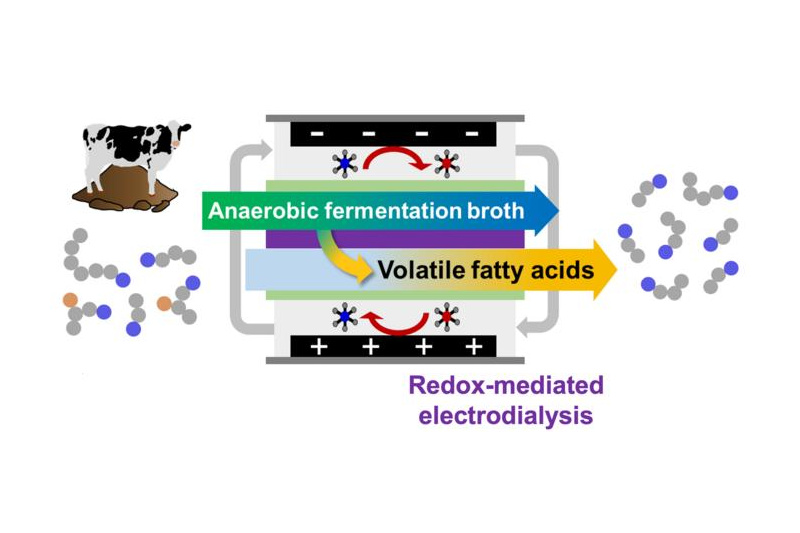
A collaboration between chemical engineers and animal scientists has created a system for recovering valuable industrial chemicals from animal waste, representing a major step towards circularity and environmental sustainability. Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a nanofiltration system for separating volatile fatty acids (VFAs) – organic molecules that are critical in fine chemical production across many sectors – from cattle manure fermented in bioreactors. Thanks to the incorporation of selective ion-exchange membranes into an electrochemical separation system,…

Findings show that radiation-induced chemistry may mitigate metal alloy corrosion in nuclear reactors cooled by molten salts High temperatures and ionizing radiation create extremely corrosive environments inside a nuclear reactor. To design long-lasting reactors, scientists must understand how radiation-induced chemical reactions impact structural materials. Chemists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and Idaho National Laboratory recently performed experiments showing that radiation-induced reactions may help mitigate the corrosion of reactor metals in a new type of reactor…

Research hints at calcium’s potential role in enforcing a specific molecular handedness among primitive polyesters and early biomolecules A new study led by researchers at the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) at Institute of Science Tokyo has uncovered a surprising role for calcium in shaping life’s earliest molecular structures. Their findings suggest that calcium ions can selectively influence how primitive polymers form, shedding light on a long-standing mystery: how life’s molecules came to prefer a single “handedness” (chirality). Like our left…

Scientists have for the first time filmed the real-time growth and contraction of Palladium nanoparticles, opening new avenues for utilising and recycling precious metal catalysts. Researchers at the University of Nottingham’s School of Chemistry used transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to observe the complete lifecycle of palladium nanoparticles in a liquid environment, from nucleation through growth to dissolution, with the entire cycle repeating multiple times. This study has been published today in Nanoscale. One of the most important applications of metal nanoparticles is…

Sugar coatings aren’t only for candies; they also help viruses, like the ones that cause COVID-19, hide from their hosts’ immune system. Now, researchers have developed a universal vaccine that targets coronaviruses and the sugars that they use as cover. As demonstrated in animal studies, the vaccine removed sugar molecules from an area of a coronavirus spike protein that rarely mutates and created effective and plentiful antibodies to inactivate the virus. Chi-Huey Wong, a chemistry professor at Scripps Research, will…

Traditionally, chemists have relied on well-established but limiting methods to synthesize these molecules. This new research presents a fundamentally different approach. Researchers at Indiana University and Wuhan University in China have unveiled a groundbreaking chemical process that could streamline the development of pharmaceutical compounds, chemical building blocks that influence how drugs interact with the body. Their study, published in Chem, describes a novel light-driven reaction that efficiently produces tetrahydroisoquinolines, a group of chemicals that play a crucial role in medicinal chemistry. Tetrahydroisoquinolines serve…

Organelles in cells were originally often independent cells, which were incorporated by host cells and lost their independence in the course of evolution. A team of biologists headed by Professor Dr Eva Nowack at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) are examining the way in which this assimilation process occurs and how quickly. They now describe their findings about an intermediate stage in this process in the scientific journal Science Advances. Eukaryotic cells – i.e. cells with a nucleus – contain…

New RNA-based active agents reliably protect plants against the Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), the most common virus in agriculture and horticulture. They were developed by researchers at the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU). The active ingredients have a broad spectrum effect; a series of RNA molecules support the plant’s immune system in combating the virus. In laboratory experiments, 80 to 100 per cent of the treated plants survived an infection with a high viral load, as the team reports in…

Innovative process converts CO2 into solid, durable, carbon-trapping materials Using seawater, electricity and carbon dioxide (CO2), Northwestern University scientists have developed a new carbon-negative building material. As Earth’s climate continues to warm, researchers around the globe are exploring ways to capture CO2 from the air and store it deep underground. While this approach has multiple climate benefits, it does not maximize the value of the enormous amounts of atmospheric CO2. Now, Northwestern’s new strategy addresses this challenge by locking away CO2 permanently and turning…

Each year billions of tons of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere by the burning of fossil fuels, certain industrial processes, construction and other human activities, creating an urgent need to find better solutions to reduce the levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide. A team of scientists led by Haotian Wang, associate professor in chemical and biomolecular engineering at the George R. Brown School of Engineering and Computing at Rice University, and Xiaonan Shan, associate professor of electrical and computer…

Mesopore introduction enables world-class hydrogen peroxide production characteristics even in low oxygen air supply environments Hydrogen peroxide is one of the world’s top 100 industrial chemicals with a wide range of applications in the chemical, medical, and semiconductor industries. Currently, hydrogen peroxide is mainly produced through the anthraquinone process, but this process has several problems, including high energy consumption, the use of expensive palladium catalysts, and environmental pollution due to by-products. In recent years, an environmentally friendly method of producing…

Hundreds of regular patterns spontaneously form on a small germanium chip Key takeaways UCLA doctoral student Yilin Wong noticed that some tiny dots had appeared on one of her samples, which had been accidentally left out overnight. The layered sample consisted of a germanium wafer topped with evaporated metal films in contact with a drop of water. On a whim, she looked at the dots under a microscope and couldn’t believe her eyes. Beautiful spiral patterns had been etched into the…

By Leah Shaffer Much of cell behavior is governed by the actions of biomolecular condensates: building block molecules that glom together and scatter apart as needed. Biomolecular condensates constantly shift their phase, sometimes becoming solid, sometimes like little droplets of oil in vinegar, and other phases in between. Understanding the electrochemical properties of such slippery molecules has been a recent focus for researchers at Washington University in St. Louis. In research published in Nature Chemistry, Yifan Dai, assistant professor of…

Butterflies are disappearing in the United States. All kinds of them. With a speed scientists call alarming, and they are sounding an alarm. A sweeping new study published in Science for the first time tallies butterfly data from more than 76,000 surveys across the continental United States. The results: between 2000 and 2020, total butterfly abundance fell by 22% across the 554 species counted. That means that for every five individual butterflies within the contiguous U.S. in the year 2000,…

Recently, a collaborative research team led by Professor WANG Hui and Professor ZHANG Xin from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, successfully developed a novel carbon-coated nickel ferrite (NFN@C) nanocatalyst with significant potential in cancer therapy. The results have been published in Advanced Functional Materials. Cancer therapy has always struggled with targeting tumor cells effectively while minimizing damage to healthy tissue. Traditional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation often have limited precision and serious side effects….