Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
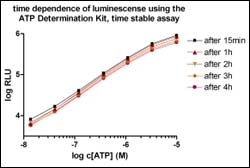
In energy consuming biological reactions the level of ATP is the essential indicator for enzyme activity or cell viability. The Biaffin ATP Determination Kits offer convenient bioluminescense assays for quantitative determination of small amounts of pre-existing ATP or ATP formed in enzymatic reactions. Catalysed by firefly luciferase the substrate D-luciferin is oxidized in an ATP-dependent process generating chemiluminescence at 560 nm (pH 7.8):

Genetically modified mosquitoes that cannot transmit malaria are one hope for battling the disease that still kills over one million people a year. But that plan faces some serious snags, according to UC Davis researchers who are suggesting an alternative strategy.
Other scientists have proposed controlling malaria by releasing into the wild mosquitoes genetically engineered to resist malaria. If the resistant mosquitoes breed and spread their genes through the population, malaria transmiss

New research findings about T-cell transport shed light on how the normal immune system functions and could have implications in fighting autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, say researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas.
Two molecules on the surfaces of T-cells – a type of immune cell – must work in tandem to help the T-cells cross from the bloodstream into infected tissues, where the T-cells initiate an immune or inflammatory response, researchers at UT Southwestern have di

International consortium provides the first step towards a comprehensive functional link between the genome sequence scaffold and human diseases
The announcement of the human genome sequence three years ago was widely hailed as one of the great scientific achievements in modern history. But sequencing the genome is just a first step — the monumental task of ascribing biological meaning to those sequences has just begun. The H-Invitational international consortium, led by Takashi Gojo

Reducing Enzyme Involved in Recycling Vitamin C Increases a Plant’s Responsiveness to Drought Conditions
University of California, Riverside researchers reported the development of technology that increases crop drought tolerance by decreasing the amount of an enzyme that is responsible for recycling vitamin C.
Biochemist Daniel R. Gallie, a professor of biochemistry at the University of California, Riverside together with Zhong Chen of his research group reported their find

Kidney disease may affect as many as one in twelve people, and causes millions of deaths each year. Currently, the diagnosis of kidney function relies mainly on blood and urine tests, an indirect means of figuring out how well they’re working.
Standard MRI scanners, used to view many organs of the body, do not always show the whole picture for kidneys. This is because the MRI equipment found in hospitals and clinics works by imaging water molecules in the body. But in water-logged kidn