Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

A new experiment by chemists from Stanford University and the University of Edinburgh has finally proven what beer lovers have long suspected: When beer is poured into a glass, the bubbles sometimes go down instead of up.
“Bubbles are lighter than beer, so they’re supposed to rise upward,” said Richard N. Zare, the Marguerite Blake Wilbur Professor in Natural Sciences at Stanford. ’’But countless drinkers have claimed that the bubbles actually go down the side of the glass. C
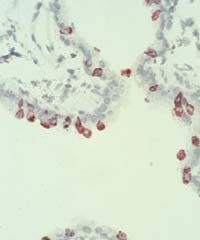
The mouse immune system develops antibodies capable of single-handedly neutralizing the SARS virus, researchers at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) report in the April 1 issue of the Journal of Virology, available online March 12. NIAID is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
This discovery affirms that researchers developing vaccines that trigger antibodies to the SARS virus are heading in the right direction. Vaccines can stimulate the immune s

Penn researchers successfully transplant cells that lead to new hair follicles
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine have isolated stem cells responsible for hair follicle growth. The findings, published in the April issue of Nature Biotechnology, may serve as the foundation for new hair loss and skin grafting treatments.
Hair grows from cells located at the base of the hair follicle. Hair follicles continuously cycle through growth, rest, and re-gr

Ancient Egyptians believed in properly equipping a body for the afterlife, and not just through mummification. A new study reveals that King Tutankhamun eased his arduous journey with a stash of red wine.
Spanish scientists have developed the first technique that can determine the color of wine used in ancient jars. They analyzed residues from a jar found in the tomb of King Tut and found that it contained wine made with red grapes.
This is the only extensive chemical analysis tha
Nanotechnology is about making improved products by building them from components hundreds of times smaller than a human blood cell. But how do you put things together at such a tiny scale? One way is to create the right conditions, so that they assemble themselves.
For example, a new method for producing uniform, self-assembled nanocells has been developed by researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Reported in the March 10 issue of the Journal of the Americ

Findings have potential implications for the use of stem cells to treat neurological diseases
A UC Irvine study on cell growth in the adult brain may provide important clues to the potential use of stem cells in the treatment of memory-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
The study shows for the first time how newborn neurons in the adult brain grow and integrate into the area involved with learning and memory. The findings may prove significant because these new neuron