Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

A new method to increase the recovery of DNA from unborn babies in a blood sample from their mothers may be helpful for future development of non-invasive prenatal genetic tests to identify fetal abnormalities, according to an article in the March 3 issue of The Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
“Prenatal diagnosis is useful in managing a pregnancy with an identified fetal abnormality and may allow for planning and coordinating care during delivery and the neonatal period,

First avian genome now available to scientists worldwide
The National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), one of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), today announced that the first draft of the chicken genome sequence has been deposited into free public databases for use by biomedical and agricultural researchers around the globe.
A team led by Richard Wilson, Ph.D., from the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis successfully assembled the genome of
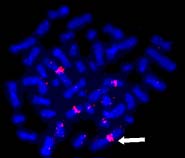
A nanoscale imaging technique that could improve the reliability of an important diagnostic test for breast cancer, and other biomedical tests, is described by National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) researchers in the Feb. 11 online issue of Nucleic Acids Research.
The method involves attaching fluorescent particles just 15 nanometers (billionths of a meter) in diameter to particular sections of DNA, followed by analysis of the intensity of the fluorescence signal and other

New research in monkeys may provide a clue about how the brain manages vast amounts of information and remembers what it needs. Researchers at Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center have identified brain cells that streamline and simplify sensory information – markedly reducing the brain’s workload.
The findings are reported in the on-line edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“When you need to remember people you’ve just met at a meeting,

Researchers have developed a method for scanning the entire human genome to successfully map the location of key gene regulators, mutated forms of which are known to cause type 2 diabetes. The research marks the first time that human organs, in this case the pancreas and liver, have been analyzed in this way and opens the door to similar studies of other organ systems and diseases.
The work, published in the Feb. 27 issue of the journal Science, could lead to new approaches for developing m

The fight against antibiotic resistance could be aided by new 3D images of the final steps involved in manufacturing proteins in living cells, scientists reveal today in a letter to Nature.
By refining a technique known as cryo-electron microscopy, researchers from Imperial College London and CNRS-Inserm-Strasbourg University have determined how the enzyme RF3 helps prepare the protein-making factory for its next task following disconnection of the newly formed protein strand.
The t