Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

The sinking of the Prestige and the resulting leakage of petroleum oil, just over a year ago, provoked a real catastrophe. A significant number of research groups were prompted to set to work to clean up the remains of this oil slick. One year after, the first results of those researches are being known. They want to use bacteria that eat petroleum oil, extracted from the proper petroleum oil.
Certain bacteria are able to feed off petroleum oil which is, in fact, full of these kinds of bact

Marvin Gaye wailed in the ’60s hit “Heard it through the Grapevine” that we’re supposed to believe just half of what we see.
Biomedical engineer Daniel Moran, Ph.D., and University of Pittsburgh researchers, have identified areas of the brain where reality and illusion are processed. For instance, the first time you don a new pair of bifocals, there is a difference in what you percieve visually and what your hand does when you reach for something. With time, though, the br
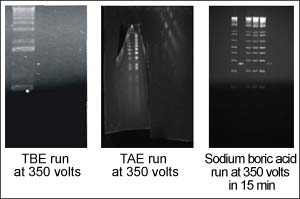
By identifying a 30-year-old mistaken assumption, Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center scientists have found that substituting a simple bleach solution for more complex tools makes a DNA separation technique called electrophoresis five times faster and less costly.
Reported in the February issue of BioTechniques, the scientists say that using the compound sodium boric acid in DNA electrophoresis may speed genetic discoveries. The scientists searched old literature and dozens of compounds to f

There sits in most mammalian cells what amounts to a lock-box of DNA tucked away from the bulk of genetic material. While scientists routinely cut and paste snippets of life’s blueprint to learn more about life and to treat disease, crucial DNA within cellular structures known as mitochondria has remained off-limits.
That’s beginning to change, though, thanks in part to work described in the Feb. 10 issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences by a team from the Un

Different combinations of genetic mutations may give rise to diverse human traits, including complex diseases such as schizophrenia, say scientists at the University of Toronto and McGill University in Montreal.
Drs. Brenda Andrews and Charles Boone of U of T and Howard Bussey of McGill used simple yeast cells to demonstrate that there are many different combinations of genetic mutations that can lead to cell death or reduced cell fitness. The research team will now focus on mapping gene int

A method for determining the function of large numbers of genes is being developed and piloted by Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) researchers at Harvard Medical School. In a trial of the technique, the researchers characterized the role in growth and viability of nearly all the genes in the genome of the fruit fly Drosophila.
Although the fruit fly genome was chosen for the first study, the researchers are confident that their technique can be applied to any organism, including humans