Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

Researchers at the University of Florida say they have shown that minerals were key to some of the initial processes that formed life on Earth.
Specifically, a borax-containing mineral known as colemanite helps convert organic molecules found in interstellar dust clouds into a sugar, known as ribose, central to the genetic material called RNA. This announcement provides a key step toward solving the 3-billion-year-old mystery of how life on Earth began. The findings will appear in Friday’s

Researchers have identified a crucial step in a genetic process required for the development of viable eggs. The process, known as imprinting, distinguishes the paternally-inherited and the maternally-inherited copies of a number of developmentally important genes.
The majority of mammalian genes are present in two copies, both of which are equally expressed and regulated. A small number of mammalian genes, however, are subject to special regulation by a process called gene imprinting. The i
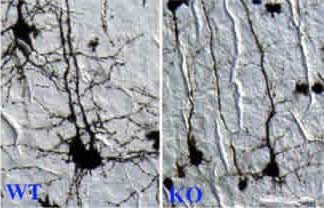
Biologists at the University of California, San Diego and the Johns Hopkins University have discovered a gene that plays a key role in initiating changes in the brain in response to sensory experience, a finding that may provide insight into certain types of learning disorders.
After birth, learning and experience change the architecture of the brain dramatically. The structure of individual neurons, or nerve cells, changes during learning to accommodate new connections between neurons. Neur

Researchers at the University of Oregon and Stanford University have located a mechanism in the human brain that blocks unwanted memories. This is the first time that anyone has shown a neurobiological basis for memory repression.
The findings, by lead researcher Michael Anderson, associate professor of psychology at the University of Oregon, and his colleague, John D.E. Gabrieli, professor of psychology at Stanford, will be published Jan. 9 in Science.
The research provides compe

Scientists at the John Innes Centre (JIC) Norwich, have discovered the molecular change that allows plants to remember winter.
Many plants need a cold period (3-8 weeks at 4° – 8°C) early in their growth to stimulate them to flower, this is called vernalisation, and without a suitable cold treatment flowering is delayed. JIC scientists have identified many of the genes involved in this process but their latest discovery is a chemical modification that occurs on one of these genes, wh

The National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), one of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), today announced that the first draft version of the honey bee genome sequence has been deposited into free public databases.
The sequence of the honey bee, Apis mellifera, was assembled by a team led by Richard Gibbs, Ph.D., director of the Human Genome Sequencing Center at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston. The honey bee genome is about one-tenth the size of the human genome, containin