Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
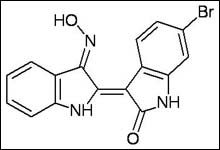
Molecule developed from marine mollusk overcomes risks of current methods
Human embryonic stem cell (HESC) lines, or cultures, in the U.S. are not suitable for use in the budding field of regenerative medicine. Their creation using mouse feeder cells, a specialized growth medium, allows scientists to study their basic characteristics, but ultimately the HESCs are too risky to develop in applied medicine because mouse-associated viruses possibly contaminate them.
Now, Rock

Ophthalmology researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a key risk factor for the development of cataracts. For the first time, they have demonstrated an association between loss of gel in the eye’s vitreous body — the gel that lies between the back of the lens and the retina — and the formation of nuclear cataracts, the most common type of age-related cataracts.
The researchers reported their findings in the January issue of Investigative Op

In four months, when flower buds spring up from the ground, you may wonder how plants know it’s time to bloom. This question has baffled plant biologists for years. Now, scientists at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have an answer: a gene that functions as an alarm clock to rouse certain plants from a vegetative state in the winter to a flowering state in the spring.
According to the researchers, the findings, published in the Jan. 8 issue of the journal Nature, could lead to new metho

Northwestern University researchers have prevented learning and memory deficits in a model of Alzheimer’s disease using a gene-targeting approach to block production of beta-amyloid, or “senile,” plaques, one of the hallmarks of the disease.
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative condition affecting over 15 million people worldwide that causes memory loss and, ultimately, dementia. Some research suggests that Alzheimer’s disease is caused by an increased amyloid burden in

Georgetown University Medical Center researchers today published the first ever fMRI study of hyperlexia, a rare condition in which children with some degree of autism display extremely precocious reading skills. Appearing in Neuron, the case study uncovers the neural mechanisms that underlie hyperlexia, and suggest that hyperlexia is the true opposite of the reading disability dyslexia.
Hyperlexia is found in very rare cases in children who are on the “autism spectrum,” meaning they

A research biologist at Wright State University is studying rhythmic cycles in birds to learn if we have a physiological clock in our stomach that determines when we get hungry.
Thomas Van’t Hof, Ph.D., an assistant professor of biological sciences, recently returned from Japan, where he presented lectures and conducted research on circadian (24-hour) rhythms in birds. He visited Okayama University of Science, a sister university of Wright State, plus the University of Tokyo and Nagoya Univ