Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

How vastly different animals arrive at the same body plan or pattern of ornamentation has long been a conundrum of developmental biology.
But now, thanks to the colorful derriere of a wild fruit fly, captured on a compost heap by a University of Wisconsin-Madison post-doctoral student, scientists have been able to document a rare example of molecular convergence, the process by which different animals use the same genes to repeatedly invent similar body patterns and structures.
W

The advantages of production in plants
According to Navarre Public University lecturer, Angel Mingo, this novel system of protein production is highly advantageous, not only due to its reduced costs with respect to cell cultures in bioreactors, but also because the method is free of the health risks associated with animal cell culture.
Moreover, the technology involved is easily accessible and enables targeting the accumulation of protein to specific compartments and organs

The complete genome sequence of a leading bacterial plant pathogen offers new ways to stave off agricultural loss and perhaps foil animal or human infection, says a Cornell University researcher.
According to Alan Collmer, Cornell professor of plant pathology, the sequencing (that is, determining the base sequence of each of the ordered DNA fragments in the genome) could help farmers repress tomato speck and other plant diseases. Medical researchers could be aided in comparing a related b
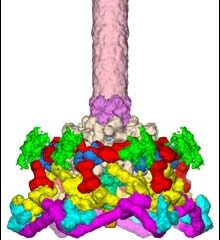
Imagine a virus and its cellular target as two spacecraft – the virus sporting a tiny docking bay that allows it to invade its victim. Purdue University researchers have taken a close-up picture of one virus’ docking bay, work that could have implications for both medicine and nanotechnology.
Using advanced imaging techniques, an international team of biologists led by Michael Rossmann of Purdue, Vadim Mesyanzhinov in Moscow and Fumio Arisaka at the Tokyo Institute of Technology has an

Findings similar to results with embryonic and neural stem cells
University of Minnesota researchers show that adult bone marrow stem cells can be induced to differentiate into cells of the midbrain. The findings, published in the online early edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggest that adult bone-marrow-derived stem cells may one day be useful for treating diseases of the central nervous system, including Parkinson’s disease.
The potent

There has been some controversy in the media and within the scientific research community concerning whether Icelanders are genetically homogenous or heterogeneous relative to other European populations.
Following an article published in Annals of Human Genetics in January 2003 by E. Árnason, who concluded that Icelanders were one of the most heterogeneous populations in Europe, researchers from deCODE Genetics and the University of Oxford, have published an article in Annals of Human Geneti