Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

The cell-surface associated molecule Cripto is overexpressed in a wide range of epithelial cancers, yet little is known about the potential mechanisms by which Cripto expression might enhance tumor growth. A new study by Michele Sanicola and colleagues at Biogen Inc. in the August 15 issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation reveals that binding of Cripto to the TGFbeta ligand Activin B can block Activin B-mediated suppression of cell proliferation. Furthermore, this study also demonstrates that

It may be small, its habitat harsh, but a newly discovered single-celled microbe leads the hottest existence known to science. Its discoverers have preliminarily named the roughly micronwide speck “Strain 121” for the top temperature at which it survives: 121 degrees Celsius, or about 250 degrees Fahrenheit. Announcing Strain 121’s record-breaking ability to take the heat in the August 15 issue of the journal Science, researchers Derek Lovley and Kazem Kashefi write, “The upper

A New Tool for Biology and Medicine
La Jolla, CA. August 14, 2003—Henry Ford revolutionized personal transportation by introducing an unusual car design onto the auto market and by embracing factory mass production of his “Tin Lizzie.”
Now a team of investigators at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) and its Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology in La Jolla, California is introducing revolutionary changes into the genetic code of organisms like yeast that allow these cel

For scientists in the field of neurobiology, defining the factors that influence the arousal of brain and behavior is a “Holy Grail.” Research published by Rockefeller University scientists in the Aug. 11 issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Early Edition are the first to give a rigorous definition of what is meant by arousal, considered to be at the base of all emotionally laden behaviors. In particular, the researchers, led by Donald W. Pfaff, Ph.D., provide an operational defi
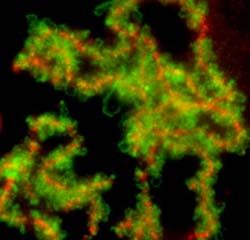
Researchers studying the nuclei of frog oocytes in early stages of meiosis — the cell division that gives rise to germ cells — have found that two key proteins remain apart at a crucial time before condensation occurs. One of the proteins, they say, may be important in the early organization of chromosomes and later may recruit the other.
In the August issue of the journal Chromosome Research, scientists at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign detail how they used antibodies to

Also found in humans – could explain why some get sicker than others
University of Michigan scientists have discovered a gene that turns a chronic inherited neurological disorder – which produces tremor and muscle weakness in laboratory mice – into a lethal disease that paralyzes and kills them within a few weeks of birth.
Called Scnm1 for sodium channel modifier 1, the gene is one of a small group of recently discovered modifier genes that interact with other genes to alte