Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

Dendritic cells monitor foreign substances in the body and communicate whether they present a danger to the rest of the immune system. Emory immunologists have developed a sensitive method to detect and follow dendritic cells by marking them with a change in their DNA, and have discovered that they are more numerous and longer lived than other scientists had previously observed. Their research uses a gene gun, which shoots DNA into the skin using microscopic gold pellets, and could lead to a faster a

Ecologists are taking to the trees in a bid to unravel the ecology of shell coiling in snails. Speaking at the British Ecological Society’s Annual Meeting, being held at Manchester Metropolitan University on 9-11 September 2003, Dr Paul Craze of the University of Plymouth will explain how examining the proportion of right- and left-coiling individuals in a species of Bornean tree snail could help ecologists understand how new species arise.
The vast majority of snail species are almost exclu

Puberty blues: goby fish choose their sex to find a mate
Research on the Great Barrier Reef has revealed that some young reef fish can choose when they mature and which sex they want to be when they grow up.
Research conducted by JP Hobbs, an honours student at James Cook University, Townsville, focused on a colourful goby that lives in bushy corals. The research may win him a British Council sponsored study tour of the UK.
Announcing his research results at Fresh Sc

A Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory physicist, in collaboration with an international team of researchers, has developed an experimental method that allows scientists to investigate the behavior of proteins under non-equilibrium conditions one molecule at a time, to better understand a fundamental biological process of protein folding that is important for many diseases.
The work, presented in the Aug. 29 edition of Science, marks the first time protein-folding kinetics has been monitor
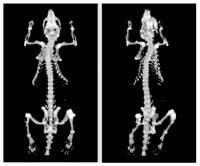
A PET (positron emission tomography) scanner sensitive enough to use on laboratory mice has been developed by biomedical engineers at UC Davis. The device is already being used for studies on prostate cancer.
“We think it’s the highest resolution scanner in existence. We can see things we couldn’t see before,” said Simon Cherry, professor of biomedical engineering at UC Davis, who leads the research group.
PET scanners have become widely used in medical imaging, alongside

Conservation International (CI) announced today the discovery of a tiny fish with a blood red tail in Venezuela’s Upper Caura River. Previously unknown to science, the bloodfin tetra (Aphyocharax yekwanae), is described in the March 2003 edition of the journal, “Ichthyological Exploration of Freshwaters.”
The two-inch-long (50.7-mm-long) tetra is only one of 10 new species of fish found during a single expedition by CI’s Aquatic Rapid Assessment Program (AquaRAP) to the Caura River Basin i