Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

A New Tool for Biology and Medicine
La Jolla, CA. August 14, 2003—Henry Ford revolutionized personal transportation by introducing an unusual car design onto the auto market and by embracing factory mass production of his “Tin Lizzie.”
Now a team of investigators at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) and its Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology in La Jolla, California is introducing revolutionary changes into the genetic code of organisms like yeast that allow these cel

For scientists in the field of neurobiology, defining the factors that influence the arousal of brain and behavior is a “Holy Grail.” Research published by Rockefeller University scientists in the Aug. 11 issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Early Edition are the first to give a rigorous definition of what is meant by arousal, considered to be at the base of all emotionally laden behaviors. In particular, the researchers, led by Donald W. Pfaff, Ph.D., provide an operational defi
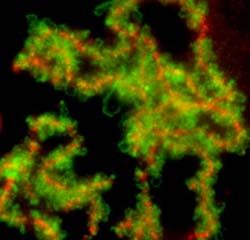
Researchers studying the nuclei of frog oocytes in early stages of meiosis — the cell division that gives rise to germ cells — have found that two key proteins remain apart at a crucial time before condensation occurs. One of the proteins, they say, may be important in the early organization of chromosomes and later may recruit the other.
In the August issue of the journal Chromosome Research, scientists at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign detail how they used antibodies to

Also found in humans – could explain why some get sicker than others
University of Michigan scientists have discovered a gene that turns a chronic inherited neurological disorder – which produces tremor and muscle weakness in laboratory mice – into a lethal disease that paralyzes and kills them within a few weeks of birth.
Called Scnm1 for sodium channel modifier 1, the gene is one of a small group of recently discovered modifier genes that interact with other genes to alte

Evolutionary biologists have developed a wide range of techniques to reconstruct the evolutionary history of particular groups of plants and animals. These techniques reveal much about the diverse patterns of evolution of life on earth, but few generalities have emerged, leading many scientists, such as the late Stephen Jay Gould, to conclude that each group of living things evolves in its own idiosyncratic manner. But now biologists at Washington University in St. Louis have proposed a general patte

A paper in Nature today (14 August) reveals that certain ocean viruses invade the cells of cyanobacteria (known as blue-green algae) and use the energy the cells produce through photosynthesis for their own purposes.
Researchers at the University of Warwick, led by Professor Nick Mann, have shown that when the viruses infect the bacteria they inject their genetic material into their host, a transfer that may be temporarily advantageous to the host.
Part of the injected DNA codes fo