Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

Birds do it, bees do it, and yes, even chimpanzees do it. They all dote on their young. And now a new theory of aging suggests that nurturing offspring is just as important as fertility and reproduction for the evolution of a species’ longevity and long-term survival.
The new theory, proposed by Ronald D. Lee, Ph.D., of University of California, Berkeley, suggests that natural selection favors animals capable of devoting energy and resources to insuring survival of the next generation.

An international project to co-ordinate human stem cell research across the globe was agreed at a 12-country* International Stem Cell Forum meeting chaired by the Medical Research Council (MRC) on Friday 11 July.
Stem cell therapy is a potentially revolutionary way to repair diseased and damaged body tissues with healthy new cells. But a huge amount of research is needed to understand how stem cells work and how their potential could be harnessed to treat conditions such as Parkinson’s dise

Scientists at Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, have unlocked an important door to understanding one of the most important crops in the world – corn. Researchers at Rutgers’ Waksman Institute of Microbiology have redefined the nature of heterosis or hybrid vigor, the phenomenon underlying corn’s remarkable success. Heterosis is the robustness seen in hybrids when different lines are crossed and result in higher yields than either of the parental lines would produce themselves.

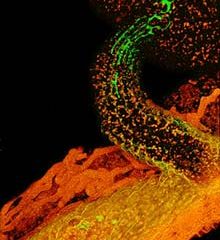
University of Chicago researchers have found that a substance that functions as a neurotransmitter in humans also plays a crucial role in plant reproduction, guiding growth of the tube that transports sperm from a pollen grain on a flower’s surface to the egg cells within a plant’s ovules.
Their finding, published in the July 11, 2003, issue of the journal Cell, is a major step forward in understanding plant fertility. The discovery could also help researchers understand similar b

Findings could improve retinal and other nervous system transplants
For the first time scientists have shown that brain stem cells are immune privileged, which means that they are invisible to a transplant recipient’s immune system and do not trigger the immune system to reject them. These results, published in the July issue of Stem Cells, indicate that using central nervous system stem cells in transplants for diseases of the eye (which is part of the brain), brain, and spinal
Nearly 80 percent of the world’s food begins as seeds, including such staple crops as corn, wheat and rice. Despite the importance and ubiquity of seeds, researchers have learned precious little about the processes that regulate plant fertilization, the essential first step in seed formation.
Now, Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) researchers have identified a key molecular signal that regulates the growth and guidance of the “pollen tube,” a tunnel formed by the pollen grain that