Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

Scientists at the University of Sheffield have cast doubt on the validity of the controversial theory of biological cold fusion, the principle sometimes used to lend credence to the practice of selling silicon tablets to strengthen bones, on the assumption that the body will turn the silicon into calcium.
Biological cold fusion, also known as the ‘Kervran effect’, is the principle that living organisms can act as alchemists and turn one element into another. The French Scientist, Louis C. Ke

The Genetic and Microbiological research group at the Navarre Public University is working with the Agruset company from Rioja in the production of new commercial varieties of the fungus oreille de chardon mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii). The same group has developed 150 new varieties of the oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus), which enhances the productivity and quality of the varieties of this fungus which are currently being commercialised.
Mushroom agreeable to the palate
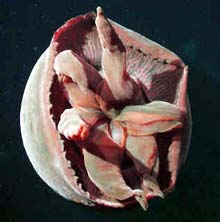
In photographs, it looks like a big red spaceship cruising the ocean depths. But it’s actually a new species of jelly that was discovered and described by scientists at the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute. MBARI scientists published their research on this unusual animal in a recent online version of the journal Marine Biology.
With a bell diameter of up to a meter wide, the new jelly, named Tiburonia granrojo or “big red,” would seem tough to miss, except that it lives deep below t

In studies that could be vital to an expanding field of industrial biotechnology, scientists at the Center for Biosystems Research are learning to censor what E.coli bacteria are ’talking’ about.
Cell-to-cell cross talking by laboratory E. coli strains engineered to produce antibiotics, industrial polymers or other products in fermentation vessels can lead to stress in the culture and severely limit product output. But scientists with CBR and partners have begun to decipher and over

Protein plays role in inherited cancer syndrome, may be key to other tumors
A research team based at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has identified a key cellular function of a protein known to be involved in the rare genetic disorder neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). The protein, called merlin, plays a key role in cell-to-cell communication and may be involved in other types of cancer. The discovery also may support the theory that some tumors are destined to spread or metastasize

One key to platelet integrin receptor found in transmembrane region
Integrin receptors allow cells to attach to other cells and to connective tissue which is necessary to form tissues, organs, or even people, for that matter. Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine have demonstrated that a key to activating αIIbβ3, the integrin that allows platelets to form blood clots, can be found in the part of the molecule embedded within a platelet’s outer