Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
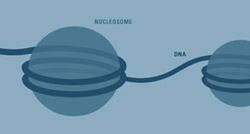
B cell chromatin study strikes physiological chord
Some cells sing with the chorus, while others unwittingly achieve fame on their own. The immune system’s B cell is a true diva that spends its early days preparing for the ultimate audition. Its repertoire of possible antibodies to invading microbes totals 50 million. For the immune system, this repertoire means the difference between destroying a potentially lethal antigen or not.
Since the late 1970s, the genes for makin

Greater insight into human brain disease may emerge from studies of a new genetic mutation that causes adult fruit flies to develop symptoms akin to Alzheimer’s disease.
“This is the first fruit fly mutant to show some of the outward, physical manifestations common to certain major human neurodegenerative diseases,” said principal investigator Michael McKeown, a biology professor at Brown University.
A research team found the mutation in a gene they named “blue cheese.” Reporting i

Increasing hormone causes increase of appetite, eating
Researchers at Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) have identified a key hormone involved in appetite control and demonstrated its effect on the brain. Scientists have shown that the hormone, called ghrelin, activates specialized neurons in the hypothalamus involved in weight regulation. The research involved scientists at several collaborating institutions, including: Yale Medical School, Baylor College of Medicine, the Uni

The universe has been mapped! Not the universe of stars, planets, and black holes, but the protein universe, the vast assemblage of biological molecules that are the building blocks of living cells and control the chemical processes which make those cells work. Researchers with the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California at Berkeley have created the first three-dimensional global map of the protein structure universe. This map provides important insight i

Montreal Neurological Institute researcher Dr. Wayne Sossin has discovered that nerve cells can bypass the cell’s normal protein-making machinery in the same way that viruses do when they infect a cell. In a study published on-line today in Nature Neuroscience, Dr. Sossin and colleagues describe the first example of regulated IRES (internal ribosome entry site) usage after a physiological stimulus in neurons.
When a virus infects a cell, its goal is to make more virus particles. To do t

A cell type with the potential for making the four major types of human tissue has been found in the stomach and small intestine by a Medical College of Georgia researcher.
These VENT cells have been found in addition to the three sources of cells typically associated with gastrointestinal development, says Dr. Paul Sohal, MCG developmental biologist, who first identified these cells nearly a decade ago.
Identification of VENT – ventrally emigrating neural tube – cells within the