Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
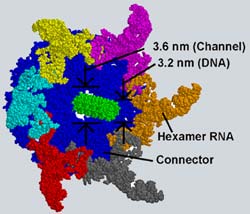
The Purdue University research team that recently created a tiny motor out of synthetic biological molecules has found further evidence that RNA molecules can perform physical work, a discovery that could advance nanotechnology and possibly solve fundamental mysteries about life itself.
Purdue’s Peixuan Guo has discovered how viral RNA molecules bind an energy-bearing organic molecule known as ATP. While linking these two substances might seem to create no more than a longer string of

Research undertaken by Professor Einar Árnason at the University of Iceland, Reykjavik and published in the January 2003 issue of Annals of Human Genetics highlights the inaccuracy of claims that Icelanders are a ’genetically homogenous’ population.
Professor Árnason explains in his article: “Recently, statements have been made about a special ’genetic homogeneity’ of the Icelanders that are at variance with earlier work on blood groups and allozymes.” Iceland has been said to be an “islan

Tequila is the national drink of Mexico and is also hugely popular worldwide. Now a Mexican student has come to England to study the unusual properties of tequila plants.
Postgraduate student Ivan Saldana Oyarzabal, from Guadalajara, which is 50km from the town of Tequila, is studying Agave tequilana and its unusual behaviour at the University of Sussex.
“These agave plants grow in extreme environments and they have a very particular behaviour,” says Ivan. “They are important plants

’Best laid plans of mice and men’
Using both the mouse and human genomes, a computer scientist at Washington University in St. Louis and international collaborators have developed a method for predicting novel genes in both genomes. With the method the scientists have discovered 1,019 novel genes that are found in both man and mouse. The breakthrough is expected to speed up discovery of genes in both genomes as well as those of other mammals. Because it is efficient and cost

In their ongoing research on turning adult stem cells isolated from fat into cartilage, Duke University Medical Center researchers have demonstrated that the level of oxygen present during the transformation process is a key switch in stimulating the stem cells to change.
Their findings were presented today (Feb. 2, 2003) at the annual meeting of the Orthopedic Research Society.
Using a biochemical cocktail of steroids and growth factors, the researchers have “retrained” specific

New method for the study and treatment of disease
The application of RNA interference (RNAi) to the study of mammalian biology and disease has the potential to revolutionize biomedical research and speed the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
A series of studies by Greg Hannon at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) have revealed a great deal of information about the mechanism of RNAi, as well as how RNAi can be adapted for use in medical research. These and other