Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

An enzyme found only in the liver and intestines may play a crucial role in the development of hardening of the arteries — or atherosclerosis, a research team from Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center and the University of California, San Francisco, report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The narrowing of arteries through atherosclerosis is a major contributor to heart attacks and strokes.
The confirmation of the relationship between the enzyme, AC

Groundbreaking study in female mice links estrogen, lower blood pressure, and insulin resistance, despite a high fructose diet
Bethesda, MD – High-fructose corn syrup replaced sucrose (table sugar) as a sweetener in most grocery products some 20 years ago. Today, about nine percent of the average dietary energy intake in the U.S. comes from fructose. However, a number of nutritionists are alarmed by the amount of the public’s consumption, as previous research has demonstrated that a

RNA interference (RNAi) has emerged as an extremely versatile and powerful tool in biomedical research. A new study published in the February issue of Nature Structural Biology reports the creation of transgenic mice in which inherited RNAi lowers or silences the expression of a target gene, producing a stable “gene knockdown.” This finding extends the power of RNAi to genetic studies in live animals, and has far-reaching implications for the study and treatment of many human diseases.
To a

Fungus-growing ants practice agriculture and have been doing so for the past 50 million years according to research published in the Jan. 17 issue of Science. These ants not only grow fungus gardens underground for food but also have adapted to handling parasitic “weeds” that infect their crops.
The team of scientists who collaborated on this analysis includes Ted Schultz of the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History, Bess Wong of the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute, Came
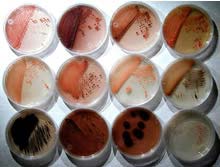
Promising cancer-fighting candidates emerge from tropical ocean ‘mud’
Although the oceans cover 70 percent of the planet’s surface, much of their biomedical potential has gone largely unexplored. Until now.
A group of researchers at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California, San Diego, have for the first time shown that sediments in the deep ocean are a significant biomedical resource for microbes that produce antibiotic molecules.
In a seri

Ground-breaking research at the University of Leicester into the division of chloroplasts holds out hope of a safer way of genetically modifying crops, with implications for agriculture particularly in the developing world.
Using three plant types – Arabidopsis, tomato and rice – Dr Simon Geir Møller has been working with colleagues in the University of Leicester Department of Biology and at the Laboratory of Plant Molecular Biology at the Rockefeller University in New York to examine how ch