Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

On 14 November ECSITE has launched BIONET (www.bionetonline.org), a European collaborative project to present for public debate controversial ethical, legal and social issues in contemporary Life Sciences.
Based on a multi-lingual website and a programme of linked events, BIONET has been developed by 8 European science centres and museums with funding from the European Commission.
The website introduces 6 current Life Science issues that raise profound ethical, legal and social dile

UCSF-led scientists have identified the first “master” molecule in the cell nucleus that controls the action of hundreds of different genes at once through its action on enzymes. The broad-acting molecule affects enzymes that restructure chromosomes, exposing genes to proteins that can then trigger key gene processes, including the start of protein production and copying and repairing of genes.
The molecule’s broad effect on a number of genes may allow organisms – including humans — to

Each spring, amid the decaying rubble of dead prairie plants, emerging male gall wasps find mates by calling upon the chemistry prowess of their predecessors, entomologists scouring Central Illinois have discovered.
In the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, they report that as adult gall wasps (Antistrophus rufus) feed in warm weather, they change the ratio of plant chemicals so that males emerging after the winter season can recognize when they are on the right stems at the r

Two specific genes involved in cholesterol transport are required for the most common way excess cholesterol is expelled from our bodies, according to scientists at UT Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas.
The genes, the researchers report, are essential for efficient secretion of cholesterol into the bile, which is the major route that cholesterol exits the body. The discovery sheds new light on potential therapies that could play an important role in reducing high cholesterol, a ma

NSF awards grants to discover the relationships of 1.75 million species One of the most profound ideas to emerge in modern science is Charles Darwin’s concept that all of life, from the smallest microorganism to the largest vertebrate, is connected through genetic relatedness in a vast genealogy. This “Tree of Life” summarizes all we know about biological diversity and underpins much of modern biology, yet many of its branches remain poorly known and unresolved. To help
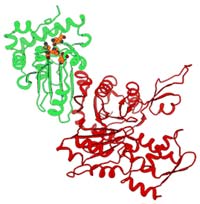
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory and their collaborators have discovered that some viruses can use the most abundant protein in the cells they are infecting to destroy the cells and allow new viruses to escape to infect others. The findings, described in the November 29, 2002, issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry, build upon earlier Brookhaven research on how virus particles become infectious (see related story) and may lead to the design of m