Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

Mushrooms (of course, those grown in an ecologically safe area) accumulate many microelements good for human and animal health, in particular, selenium. The natural cycle of selenium was studied by a team from the Vernadsky Institute of Geochemistry and Analytical Chemistry in Moscow.
The scientific expedition worked in the eastern part of the Meshchera (at the meeting point of the Moscow, Ryazan, and Vladimir areas). Scientists found selenium in many natural objects (soil, grass, le

Because living organisms contain millions of different molecules, identifying or separating any single one of these from their natural environment in order to carry out research work or perform diagnoses is quite like looking for a needle in a haystack. A number of molecular separation technologies are of course available, and are used by laboratories on a daily basis, but they are often unwieldy and costly. Scientists the world over are therefore attempting to develop a new generation of analytic de

Formidable catalogue puts army of ants online.
After four years of cooperation and tenacity worthy of their quarry, ant experts have completed Antbase, a centralized, online information resource cataloguing all 11,000 known species of ant.
Its creators hope that Antbase will one day become the ant equivalent of GenBank, the public database of genetic sequence data, and a boon not just for ant specialists, but for entomologists and ecologists of every kind.
Ant ta
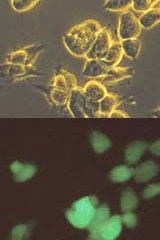
Fusion may explain adult stem-cell morphing.
The hyped ability of adult stem cells to sprout replacement tissue types is being called into question. They may instead be fusing with existing cells, say two new reports, creating genetically mixed-up tissues with unknown health effects.
Recent studies have shown that adult stem cells transplanted from one tissue, such as blood, can spawn the cell types of another, such as nerves. The findings have stirred intense interest in st
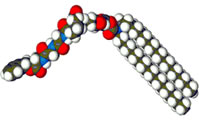
Chemists copy from cells to make a tunnel for salt
Chemists have finally achieved what every human cell can do. They have designed and built from scratch a gate for electrically charged chlorine atoms to pass through 1 .
George Gokel and colleagues at Washington University in St Louis, Missouri, based their gate on biological proteins that transport chloride ions from one side of our cell membranes to the other. Like these, the synthetic channel can be opene

Many chemicals commonly used in medications such as over-the-counter painkillers or birth control pills end up far from their intended destination – in American streams. According to a new report, published online today by the journal Environmental Science and Technology, a number of the waterways contain complex cocktails of compounds.
The 30-state study, conducted by the U.S. Geological Survey, tested 139 streams for 95 organic contaminants – ranging from medications and hormones to inse