Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

Humans learn water-gathering trick from bumpy beetle.
A desert beetle turns fog into drinking water with its wings, new research reveals. Materials mimicking the insect could help humans survive harsh environments.
Southwest Africa’s Namib Desert is one of the hottest and driest places on Earth. There is no rain, but on about six mornings a month a fog blows in off the Atlantic and across the land at gale force.
The beetle Stenocara traps this fleeting resour
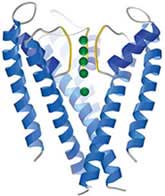
Dazzling snapshots show how ions power nerve signals round the body.
“Potassium channels underlie all our movements and thoughts,” says Rod MacKinnon of Rockefeller University in New York. His team has now unravelled the molecular mechanics of these minute protein pores. Some say the work merits a Nobel Prize.
Potassium (K + ) channels power the transmission of nerve signals through the body and the brain by ushering K + ions in and out of our cells. MacKin

Researchers have put a new face on what may be an old genetic weapon to help plants fight off a pesky infection. Abhaya Dandekar and colleagues at the University of California at Davis gave plants an extra gene that protected them from crown gall disease—a scourge of the walnut, grape and rose, among others—when tested in the lab. They publish their findings today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. When the bacterium that causes crown gall disease enters a plant, it starts

New light-sensitive glass can be recycled cleanly.
Researchers in Japan have developed recyclable light-sensitive glass. The new ’ecoglass’ does not contain the environmentally damaging halogen elements chlorine, bromine or iodine. These elements are essential to the photochromic glass that is currently used for car windscreens, sunglasses and visual display units.
Like photographic film, today’s photochromic glasses darken because they contain compounds of silver and halog

Army ants team little with large to lift heavy loads.
If you can’t see the point of the miniature back wheel on a penny-farthing bicycle, try riding a unicycle or watch an ant colony. Ants have realized that, to carry a heavy load, two supports are better than one – even if they seem comically mismatched.
When army ants partner up to carry a lump of food too big for a single ant to transport, an unusually large worker ant takes the front, and an unusually small one, the back

Draft Fugu genome will help find human genes.
A draft sequence of the puffer-fish genome is complete. The fish’s compact genetics should accelerate the discovery of human genes and their key controlling sequences.
Gene-prediction programs struggle to find genes in the 3 billion letters of the human sequence, which includes swathes of junk DNA and defunct pseudogenes.
The bony fish Fugu rubripes shares our gene repertoire but has a genome one-eighth of the size.