Possible physical trace of short-term memory found
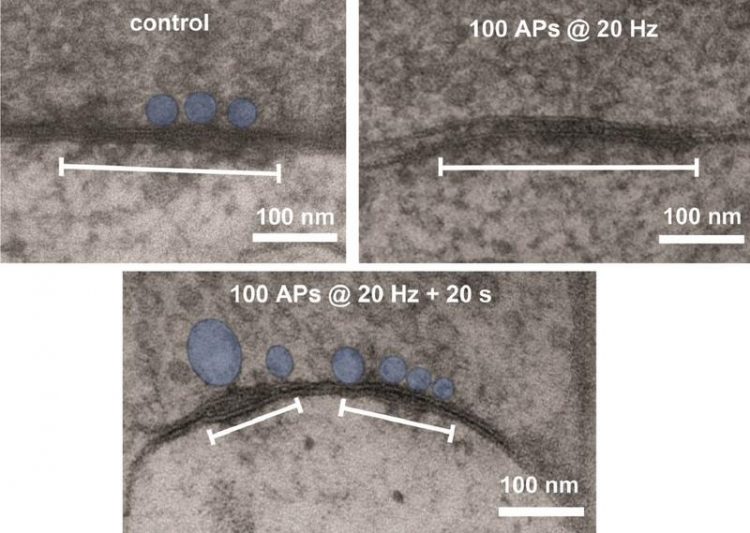
A photo of the potential engram: Without activity, only few vesicles are found at the synapse. After a short burst of activity, vesicles dock at the synapse. The pool of vesicles is stored at the synapse even minutes later. This pool may be the physical trace of memory, the “engram”. © Jonas Group / IST Austria
Already Plato and Aristotle asked how memory is stored as changes in the brain. In a new study, Professor Peter Jonas and his group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (IST Austria), including first author David Vandael, found that short-term memory may be formed by storing vesicles of neurotransmitter.
These vesicle pools could be an “engram,” a physical trace of memory. The study is published in the journal Neuron.
Forming memory is essential for us to learn and acquire knowledge. In the 20th century, Richard Semon introduced the idea of an “engram,” a physical substrate of a memory: as an animal learns, information is stored in an engram in the brain. Later, this information is retrieved.
“Where are the engrams? This was one of the questions we asked”, explains Peter Jonas. “Synaptic plasticity, the strengthening of communication between neurons, explains memory formation at the subcellular level. To find the engram, we, therefore, explored structural correlates of synaptic plasticity.”
Unexpected mechanism strengthens communication
For this search, postdoc David Vandael studied single synapses in the hippocampus, the brain area required for learning and memory. Among the many synapses that connect with a pyramidal cell neuron in the hippocampus, Vandael picked out one and recorded what happens as a granule cell sends a signal to the pyramidal cell it connects with.
“Recording from single identified synapses is crucial. We, therefore, set up a close-to-impossible experiment, in which we made simultaneous recordings of electrical signals from a small pre-synaptic terminal and its postsynaptic target neuron. This is the perfect way to examine the synapse”, Vandael illustrates.
Vandael found that when a granule cell fires, it induces a type of synaptic plasticity called post-tetanic potentiation, which strengthens communication between granule cell and pyramidal cell for several minutes.
However, the mechanism behind this plasticity was unexpected: based on what others had found for a model synapse, the calyx of Held, Vandael, and Jonas had hypothesized that plasticity arises because, after a burst of activity, vesicles would be more likely to release neurotransmitters into the synapse.
This release of neurotransmitter is how signals are transmitted from one neuron to the other. “Instead, we found that after a granule cell is active, more vesicles containing neurotransmitter are stored at the pre-synaptic terminal,” Vandael explains.
“Firing patterns induce plasticity through an increase of vesicles in this active zone, which can be stored for a few minutes.”
Vesicle pools as an engram for short-term memory?
During learning, when the granule cell is active, vesicles are pushed into this pool at the active zone. When activity drops, the vesicles stay in the pool. When activity resumes, more vesicles stored in the active zone means more transmitter is released into the synapse.
“Short-term memory might be activity stored as vesicles that are released later,” Vandael adds.
In the end, this might be an important discovery, Jonas says. “By analyzing the biophysical and structural components of plasticity, David may have discovered the engram – if we believe that synaptic plasticity underlies learning.”
In further work, the group currently tries to correlate synaptic signals in vivo with behavioral changes.
The new findings help expand our understanding of learning and memory, Vandael says. “It is fascinating to think of memories as numbers of neurotransmitter-containing quanta, and we truly believe it will be inspiring for the neuroscience research community. We hope our work will contribute to solving part of the unresolved mysteries of learning and memory.”
Getting to grips with how different synapses work may also help to understand how diseases affect synapses, Jonas adds.
David Vandael, Carolina Borges-Merjane, Xiaomin Zhang, and Peter Jonas. 2020. Short-term plasticity at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses is induced by natural activity patterns and associated with vesicle pool engram formation. Neuron. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.05.013
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Redefining Cancer Science: Rodents, Humans, and the PD-1 Puzzle
Results of a comprehensive analysis refute assumptions that a key immune checkpoint receptor functions the same in rodents and humans The Discovery of PD-1: A Milestone in Cancer Treatment Since…

Heart Surgery Risks: Low BP Linked to Postoperative Kidney Injury
First large cohort study at the Heart and Diabetes Center NRW awarded – Hilke Jung presents research project at the FoRUM conference of the Ruhr University Bochum A working group…

Microbial Secrets: Boost Plant Growth with the Power of Soil Bacteria
To stay healthy, plants balance the energy they put into growing with the amount they use to defend against harmful bacteria. The mechanisms behind this equilibrium have largely remained mysterious….



