Printing technique creates effective skin equivalent, heals wounds
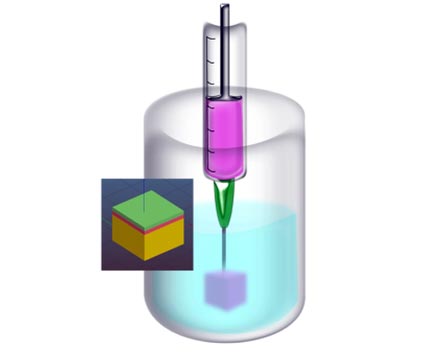
The suspended layer additive manufacturing technique uses gel to support the skin equivalent as it is printed.
Credit: Moakes et al.
Material mimics all three layers of the skin, allows for complex printing structures.
Chronic wounds are deep and difficult to repair. Often, the top of the injury heals before the bottom, so the wound collapses in on itself. Over time, this can result in scar tissue and reduced skin function.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Birmingham and University of Huddersfield developed an approach to print skin equivalents. The material may play a future role in facilitating the healing of chronic wounds.
The technique is the first of its kind to simulate three layers of skin: the hypodermis, or fatty layer, the dermis, and the epidermis.
“You effectively have three different cell types. They all grow at different speeds,” said author Alan Smith. “If you try to produce tri-layered structures, it can be very difficult to provide each of the requirements of each different layer.”
To solve this problem, the scientists used suspended layer additive manufacturing (SLAM). They created a gel-like material to support the skin equivalent, twisting and altering the structure of the gel as it formed to create a bed of particles that can then support a second phase of gel injection.
During printing, the skin layers are deposited within the support gel, which holds everything in place. After printing, the team washed away the support material, leaving behind the layered skin equivalent.
If the researchers moved a needle through the supporting gel, it repaired itself faster than other similar techniques. This results in higher resolution printing than previous methods and allows for the printing of complicated skin structures.
The authors tested the skin substitute by cutting a hole in pig tissue and printing a skin equivalent to fill the hole. After culturing the model system for 14 days, they saw signs of wound repair.
“We used a stain that allowed us to quantify the integration we got between original material and tissue,” said author Liam Grover. “We were able to demonstrate some integration even after a short period of time.”
The team cannot assess chronic wound healing with the skin substitute because that process takes more time than their model allowed, which was only 14-21 days. However, their next step is to test longer, appropriate models for chronic deep wounds. The ultimate goal is to repair human skin and reduce scarring for all patient scenarios.
The article “A suspended layer additive manufacturing approach to the bioprinting of tri-layered skin equivalents” is authored by Richard J.A. Moakes, Jessica J. Senior, Thomas E. Robinson, Miruna Chipara, Aleksandar Atansov, Amy Naylor, Anthony D. Metcalfe, Alan M. Smith, and Liam M. Grover. The article appeared in APL Bioengineering on Nov. 30, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0061361) and can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/5.0061361.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Bioengineering is an open access journal publishing significant discoveries specific to the understanding and advancement of physics and engineering of biological systems. See http://aip.scitation.org/journal/apb.
Journal: APL Bioengineering
DOI: 10.1063/5.0061361
Article Title: A suspended layer additive manufacturing approach to the bioprinting of tri-layered skin equivalents
Article Publication Date: 30-Nov-2021
Media Contact
Larry Frum
American Institute of Physics
media@aip.org
Office: 301-209-3090
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



