Rapid evolution: New findings on its molecular mechanisms
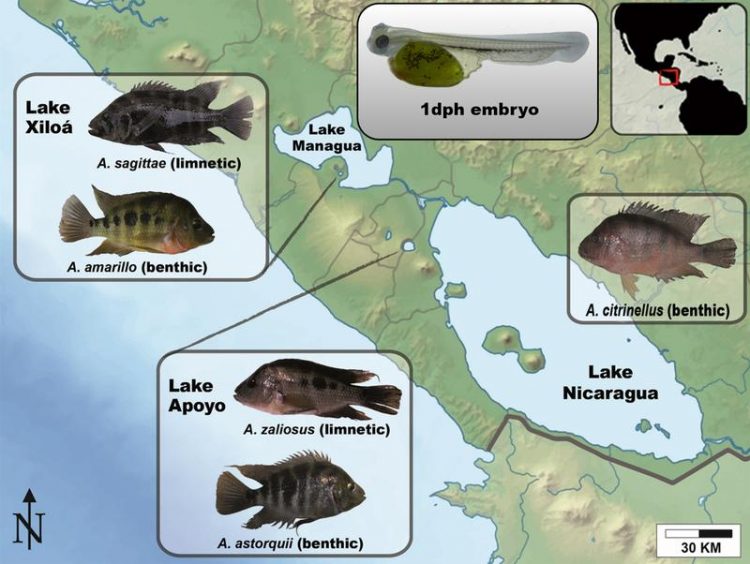
The Midas cichlid fish from the crater lakes of Nicaragua are one of the the best known examples for sympatric speciation. They evolved from a source population into a variety of independent species in less than 22,000 years. University of Konstanz
The mechanisms by which new species arise are still not fully understood. What are the evolutionary processes that drive the evolution of new species? Evolutionary biologists traditionally assumed that geographical barriers between animal populations play a decisive role (allopatric speciation): a species is physically separated into two or more isolated populations, thereby preventing gene flow between these groups.
The subpopulations adapt to their respective habitats and evolve into independent species with different characteristics. In recent years, however, the evolutionary biologist Professor Axel Meyer from the University of Konstanz has not only been able to show that new species can evolve from a source population within a shared habitat and in the presence of gene flow (sympatric speciation), but that this type of speciation might be much more common than previously thought.
His laboratory is investigating both the ecological and genetic mechanisms that facilitate sympatric speciation. In a recent publication in the scientific journal Molecular Biology and Evolution, Axel Meyer and his colleagues Paolo Franchini, Peiwen Xiong, Carmelo Fruciano, Ralf Schneider, Joost Woltering and Darrin Hulsey identify the decisive role that a kind of genetic switch, microRNAs, play in sympatric speciation.
Rapid evolution of cichlids
The researchers led by Axel Meyer analyze the Midas cichlid fish from Nicaragua's volcanic crater lakes as a model system in their research. Cichlids are known for their ability to adapt to new environments at an exceptionally rapid rate and to form new species.
The new fish species originate from a population found in the large lakes of Nicaragua, but after colonizing several very small and young crater lakes, they adapted to new ecological niches, evolved new characteristics (e.g. a more elongated body or a different jaw) and evolved into a variety of new species in less than 22,000 years.
A further distinctive feature of these Midas cichlids is that they evolved into different species within the same population, sometimes repeatedly, by adapting to different ecological niches within their small crater lakes. The Midas cichlids of Nicaragua are thus one of the best known examples for sympatric speciation.
Within such a short time period new mutations are very unlikely to happen. This made finding a molecular mechanism that can bring about different body shapes, adaptations and thereby distinct ecological niches so difficult and interesting. The evolution of microRNAs and new target sites for them to regulate the expression of genes offers one potential molecular mechanism that can bring about very fast evolutionary change with very little genetic differences between the extremely young species.
microRNA
The biologists from Konstanz carried out genetic analyses of five species of Midas cichlids from the crater lakes Apoyo and Xiloá. Here, they focused in particular on the function of the so-called microRNA – a non-coding ribonucleic acid that has a regulatory effect on gene expression. The researchers found an increased activity of microRNA in young fish one day after they hatched during a phase in which the fish bodies are formed.
They analyzed the interaction between microRNA and gene expression, identifying specific pairs of microRNAs and genes that influence each other. The microRNA suppresses the expression of the target genes and thus has a regulatory effect on them: the more active a particular microRNA is, the more effectively the target gene is suppressed or “switched off”. “Our research results provide strong evidence that extremely quickly evolving microRNA regulation contributes to the rapid sympatric speciation of Midas cichlids,” says Paolo Franchini.
Facts:
– Evolutionary biologists from Konstanz investigate the role of microRNA in the rapid sympatric speciation of Midas cichlids – the evolution of new species within the same habitat and in the presence of gene flow.
– Original publication: Paolo Franchini, Peiwen Xiong, Carmelo Fruciano, Ralf F Schneider, Joost M Woltering, C Darrin Hulsey, Axel Meyer, MicroRNA gene regulation in extremely young and parallel adaptive radiations of crater lake cichlid fish, Molecular Biology and Evolution, msz168
Link: https://academic.oup.com/mbe/advance-article/doi/10.1093/molbev/msz168/5545549
– Genetic analyses of five species of Midas cichlids from the crater lakes Apoyo and Xiloá, which evolved out of a shared source population into new species in far less than 22,000 years.
– Analyses of the interaction between microRNA and genes. Specific pairs of microRNAs and genes that interact with each other were identified. The microRNA suppresses the expression of the target genes.
– This research project was carried out in the context of Professor Axel Meyer’s ERC Advanced Grant “Comparative genomics of parallel evolution in repeated adaptive radiations” (GenAdap 293700). The project was also funded by a German Research Foundation (DFG) grant (FR 3399/1-1).
Note to editors:
You can download pictures here:
https://cms.uni-konstanz.de/fileadmin/pi/fileserver/2019/Bilder/Evolution_1.jpg
Caption: The Midas cichlid fish from the crater lakes of Nicaragua are one of the the best known examples for sympatric speciation. They evolved from a source population into a variety of independent species in less than 22,000 years.
https://cms.uni-konstanz.de/fileadmin/pi/fileserver/2019/Bilder/Evolution.jpg
Caption: Researchers found an increased activity of microRNA in young fish one day after they hatched.
Prof. Axel Meyer, Dr. Paolo Franchini
University of Konstanz
Paolo Franchini, Peiwen Xiong, Carmelo Fruciano, Ralf F Schneider, Joost M Woltering, C Darrin Hulsey, Axel Meyer, MicroRNA gene regulation in extremely young and parallel adaptive radiations of crater lake cichlid fish, Molecular Biology and Evolution, msz168
Link: https://academic.oup.com/mbe/advance-article/doi/10.1093/molbev/msz168/5545549
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



