Exosomes, novel antigen bearers in "antitumor vaccination", yield some of their secrets
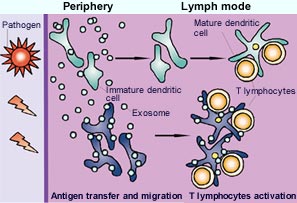
Working model for the role of exosomes in immune responses. <br>After the uptake of incoming pathogens in the periphery, immature or maturing dendritic cells (green) generate peptide-MHC complexes. Some of these complexes could be secreted on exosomes, and locally sensitize other dendritic cells (blue) that have not encountered the pathogen directly. As a result of the effects of inflammation, all of these dendritic cells migrate out of the tissue towards the draining lymph nodes. Although maturing dendritic cells seem to secrete fewer exosomes than immature cells, an exchange of exosomes inside the lymph nodes between newly arrived (and not fully mature) and resident dendritic cells could take place also. Therefore, exosome production would increase the number of dendritic cells that bear the revelant peptide-MHC complexes, and thereby amplify the magnitude of immune responses. In the absence of inflammation, spontaneous migration of exosome-bearing dendritic cells could contribute to tolerance induction. <br>
Exosomes are minute, natural membrane vesicles secreted by various types of cells of the immune system. They are of enormous interest to oncologists, who are now using them in clinical trials as tumor-antigen bearers to trigger tumor rejection by the body.
On the basis of studies in vitro and in mice, INSERM doctors and research scientists at the Institut Curie proposed a novel mode of functioning of exosomes in the December 2002 issue of Nature Immunology. It seems that exosomes can indirectly stimulate the immune system. When they are secreted by dendritic cells (the immune system’s “sentries”), they are captured by other dendritic cells, which subsequently bring about the triggering of the immune response. It is as if one of the functions of the exosomes is to transfer their specific membrane-borne antigens to other dendritic cells, thus multiplying the number of “sentries” alerted and raising the defense potential of the immune system. If this mechanism is confirmed, it would partly explain how exosomes participate in tumor rejection in vivo.
These studies will undoubtedly lead to improvements in the use of antigen-bearing exosomes in cancer immunotherapy.
At the Institut Curie, a research group (Clotilde Théry, Sebastian Amigorena) and a medical team (Livine Duban, Olivier Lantz) (1) have joined forces to study the mechanisms of action of mouse dendritic cell-derived exosomes. At their surface these exosomes present several proteins involved in the stimulation of target T-cells (including molecules of the major histocompatibility complex or MHC), as well as a specific antigen. The Institut Curie teams confirmed that T-cells bearing a surface receptor to this specific antigen are directly stimulated in vivo, thus triggering the immune response. They noted, however, a strange phenomenon: exosomes only induce the proliferation of T-cells in vitro if “mature” dendritic cells are also present.
Do exosomes transfer antigens?
To explain this behavior, the authors propose that once they are produced the exosomes derived from “immature” dendritic cells will be captured by “mature” dendritic cells. The MHC-antigen complex is transferred from the exosomes to these dendritic cells, which then activate the appropriate T lymphocytes.
What is the benefit of such a strategy for the organism? The authors suggest that the exosomes may be secreted into the peripheral tissues where the dendritic cells meet pathogenic agents (viruses, bacteria, tumor cells) and migrate from there towards the lymph nodes where they sensitize mature dendritic cells. The exosomes could therefore “prime” several mature dendritic cells and hence increase the number of cells presenting the antigen to the T lymphocytes (diagram p.3). For the moment, however, this remains hypothetical since the secretion of exosomes by dendritic cells in vivo has not been formally demonstrated. In contrast, exosomes (first described almost 20 years ago) are clearly secreted in vitro.
What is important is that we can induce cells to secrete exosomes in vitro, i.e. in large quantities, and then use these exosomes to elicit in vivo specific immune reactions and not generalized activation of the immune system.
Highly characteristic but mysterious vesicles
Exosomes are flattened spheres, bounded by a lipid bilayer, that are secreted by the cell on the fusion of small internal compartments with the plasma membrane. They are smaller (30 to 100 nm in diameter) than other cell-secreted membrane vesicles.
The protein composition (internal or membrane) of exosomes is also characteristic and now quite well established: adhesion, transport, membrane fusion and signal transduction proteins, plus the proteins that bind and present the antigen. The precise function in the exosomes of most of these proteins remains unclear. The biological function of the exosomes themselves is also uncertain, although credible hypotheses can be built on the data accumulated in recent years.
Stimulatory activity and promising clinical trials
Several types of cells seem able to secrete exosomes, particularly certain cells of the immune system (mastocytes, T and B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, platelets).
In 1996, a pioneering team observed in vitro that exosomes derived from human B lymphocytes stimulate T lymphocytes, by presenting to them a specific antigen (2).
In 1998, a collaboration between scientists at the Institut Curie and the Institut Gustave-Roussy showed that exosomes, produced in vitro by dendritic cells previously pulsed with tumor antigens, induce tumor rejection in mice (3).
One of the lines of research then focused on the use of these exosomes as a “vaccine” in the prevention of tumor recurrence caused by cancer cells that elude the effects of treatment.
After the positive findings recorded in mice, a first phase I clinical trial (to determine toxicity and effective dose in a small number of patients) was launched in France in 2000, at the Institut Curie and at the Institut Gustave-Roussy. Exosomes bearing the melanoma antigen MAGE3 were administered to patients with metastatic melanoma expressing MAGE3. No toxicity was seen, but there was a positive response in the patients receiving the highest doses: regression of skin tumors in some and reduction of lymph node metastases in others.
A second phase I clinical trial is currently under way in the United States, at Duke University. Dendritic cell-derived exosomes are being administered to patients with non-small cell lung cancer. The preliminary results show prolonged stabilization of the disease.
Another phase I trial should begin in France in 2003, using exosomes in the treatment of cancer of the neck of the womb.
Finally, the American authorities have just approved a planned Franco-American, multicenter (Institut Curie, Institut Gustave-Roussy and several American hospitals) phase II trial in patients with advanced melanoma or non-small cell lung cancer.
Reference
“Indirect activation of naïve CD4+T cells by dendritic cell-derived exosomes”
Clotilde Théry*, Livine Duban*°, Elodie Segura*, Philippe Véron*, Olivier Lantz*° and Sebastian Amigorena*
Nature Immunology, vol 3, no. 12, December 2002
* Unité INSERM 520, Institut Curie. ° Laboratoire d’Immunologie Préclinique, Institut Curie
Notes
(1) Unité INSERM 520 “Cellular biology of tumoral immunity” headed by Christian Bonnerot, Research division of Institut Curie and Preclinical Immunology Laboratory, Medical division of Institut Curie.
(2) “B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles” Raposo, G., Nijman, H.W., Stoorvogel, W., Liejendekker, R., Harding, C.V., Melief, C.J. and Geuze, H.J. Journal of Experimental Medicine. Vol 183, 1161-72, 1996
(3) “Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes” L. Zitvogel, A. Regnault, A. Lozier, J. Wolfers, C. Flament, D. Tenza, P. Ricciardi-Castagnoli, G. Raposo & S. Amigorena – Nature Medicine, Vol.4, No. 5, 594-600, May 1998
Press contacts
Institut Curie
Press Office
Catherine Goupillon
Phone 01 44 32 40 63
service.presse@curie.fr
Iconography
Cécile Charré
Phone 01 44 32 40 51
Fax 01 44 32 41 67
Inserm
Press Center
Céline Goupil
Phone 01 44 23 60 73
presse@tolbiac.inserm.fr
Séverine Ciancia
Phone 01 44 23 60 86
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



