Research reveals potential new target for prostate cancer drugs
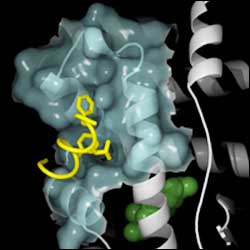
This atomic-level model of part of the human androgen receptor shows the target for a potential drug against prostate cancer. New research has determined the three-dimensional, atom-by atom structure of the target. The drug would bind to the receptor, interrupting its activity which drives the disease.
Scientists have determined the precise molecular structure of a potential new target for treating prostate cancer, a disease driven in part by abnormal testosterone activity. The target is part of the androgen receptor, a protein essential for testosterone to function in human cells. Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men.
The androgen receptor and testosterone – technically, 5-alpha dihydrotestosterone – each drive prostate cancer at different stages of the disease. A common prostate cancer treatment uses drugs that compete with testosterone, blocking its ability to bind with the androgen receptor and so reducing the hormone’s effect. But cancer tends to become resistant to these drugs. The new research provides a novel strategy to block activation of both the androgen receptor and testosterone.
UCSF scientists determined the atom-by-atom topography of the pocket where proteins known as coactivators bind to the human androgen receptor to enable testosterone to trigger gene activity. Knowing the detailed shape greatly boosts the likelihood of developing a drug to block this binding and turn off androgen receptor activity, the scientists report.
The research is being published online August 24 by Public Library of Science (PLoS) Biology. “Drugs that block testosterone binding are not effective in the long term against prostate cancer,” says Robert Fletterick, PhD, UCSF professor of biochemistry and biophysics and senior author on the PloS Biology paper. “The shape of the site we have determined – where coactivators bind to the androgen receptor – specifies the design for a new class of drugs. Simple versions of the ’ultimate’ drug will be tested in cancer cells this year.” With an aggressive search for the right chemicals, candidate drugs might be tested in human patients within three years, he says.
UCSF has filed for a patent revealing the nature of the coactivator site on the androgen receptor.
Fletterick, whose laboratory is based at UCSF’s Mission Bay campus, is a researcher in the California Institute for Quantitative Biomedical Research, or QB3. He collaborates with clinical cancer scientists at UCSF, and the new research is supported by an NIH SPORE grant (for Specialized Program of Research Excellence), which funds programs that effectively integrate basic research, such as Fletterick’s, with clinical research aimed at developing new clinical treatments. Fletterick’s UCSF clinical research colleagues are eager to work on developing treatments if coactivator-blocking drugs can be developed, he says.
The male hormone testosterone controls development and maintenance of the male reproductive system and other tissues such as bone and muscle. The hormone is present in smaller amounts in females, where it also helps form muscle and bones.
The scientists determined the shape of the binding pocket on the androgen receptor – technically, the coactivator binding interface – by exposing it to billions of randomly chosen protein fragments, or peptides, and selecting for those that bind best. They then imaged the peptides that bind best using a technology called X-ray diffraction that shows every atom of the peptide and the receptor, and how they interact.
The researchers are now testing the ability of different small molecules to bind to the androgen receptor binding site. They hope to demonstrate the potential of developing a drug that will bind more strongly than the normal coactivator, thereby shutting down androgen receptor activity.
Knowing the molecular shape of the target speeds development of a new drug about ten-fold, Fletterick says, and helps assure that the drug will work as expected. The new structural information from the limited number of peptides and small molecules that bind well to the coactivator sites can be used by chemists to screen from among thousands of “best-fitting” molecules to find those with the precise configuration and traits needed for a good drug to block coactivator binding, Fletterick says. In addition, chemists can use the information to synthesize new molecules with the required drug traits.
It remains uncertain whether researchers can identify a small molecule drug candidate that binds to the coactivator more strongly than the coactivators themselves do, Fletterick cautions.
Cancer researchers do not know which coactivators bind with the androgen receptor when cancer strikes, Fletterick adds. But the research may lead to selective drugs that permit “good” activators to bind while blocking those that promote cancer progression. This possibility is the focus of new research by several UCSF labs.
The highly detailed structure of the coactivator binding site revealed by the research explains the unusual behavior of this hormone’s receptor, says Eugene Hur, BS, UCSF graduate student in biophysics and lead author of the scientific paper. Most hormone receptors bind to coactivator sequences rich in the amino acid leucine, but the androgen receptor is unique in preferring bigger, bulkier bonding partners. The explanation appears to lie in the unusually deep binding region, the scientists report.
Co-authors on the paper, along with Fletterick and Hur, are Samuel J. Pfaff, BS, graduate student in biophysics at UCSF; E. Sturgis Payne, research staff; Hanne Gron, PhD, research scientist; and Benjamin M. Buehrer, PhD, project leader, all at Karo Bio in Durham, North Carolina.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.ucsf.eduAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Parallel Paths: Understanding Malaria Resistance in Chimpanzees and Humans
The closest relatives of humans adapt genetically to habitats and infections Survival of the Fittest: Genetic Adaptations Uncovered in Chimpanzees Görlitz, 10.01.2025. Chimpanzees have genetic adaptations that help them survive…

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…



