Waves make bug break point
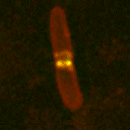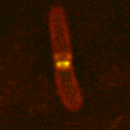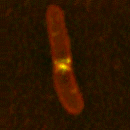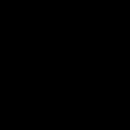
Formation of the Z ring as an E. coli cell divides. <br>© Qin Sun/University of Texas <br>
Sloshing proteins help bacteria find their waists.
Chemical waves may help a bacterium to divide by pinpointing its middle, according to a new model of protein interactions1.
Bacteria such as Escherichia coli multiply by dividing. Bacterial division (called binary fission) is simpler than human cell division (mitosis). Human cells erect scaffolding to transport components to the two nascent daughter cells at either end; bacteria just pinch in two.
Within this simplicity lies a puzzle. Without sophisticated molecular machinery, how do bacteria organize themselves so that their daughter cells are of roughly equal size?
Martin Howard of Simon Fraser University in Burnaby, British Columbia, and colleagues think that the key is in the sloshing of three proteins, MinC, MinD and MinE, from end to end of the bacteria. This Min family initiates the formation of a protein drawstring, the Z ring, that runs around the cell’s midpoint and contracts to form a narrow waist.
In an E. coli cell, the Min proteins interact, setting up waves that sweep from end to end with a period of about 1-2 minutes. MinC and MinD gather at the cell’s ends, MinE gathers in the middle. MinC disrupts Z-ring formation, so the ring appears only at the midpoint, where the MinC concentration is low.
Howard’s team has devised a mathematical model of the Min family’s interactions. The model shows that the proteins’ oscillations can produce standing waves, like the air waves in an organ pipe, with MinE concentrated in the cell’s middle and MinC and D at the ends.
A similar interplay between reacting and diffusing proteins during development is thought to be responsible for some animals’ stripes. If Min proteins were coloured, a dividing bacterium would be dark at each end with a light band in the middle.
The researchers say that reasonable assumptions about the rates of protein reactions and diffusion give the right single-band form – two bands of MinE, for example, would result in a cell being pinched into three daughter cells. But they acknowledge that these rates have not yet been measured accurately enough to test the model stringently.
References
- Howard, M., Rutenberg, A. D. & de Vet, S. Dynamic compartmentalization of bacteria: accurate division in E. coli. Physical Review Letters, 87, 278102, (2001).
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nature.com/nsu/011220/011220-7.htmlAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



