Researchers build embryo-like structures from human stem cells
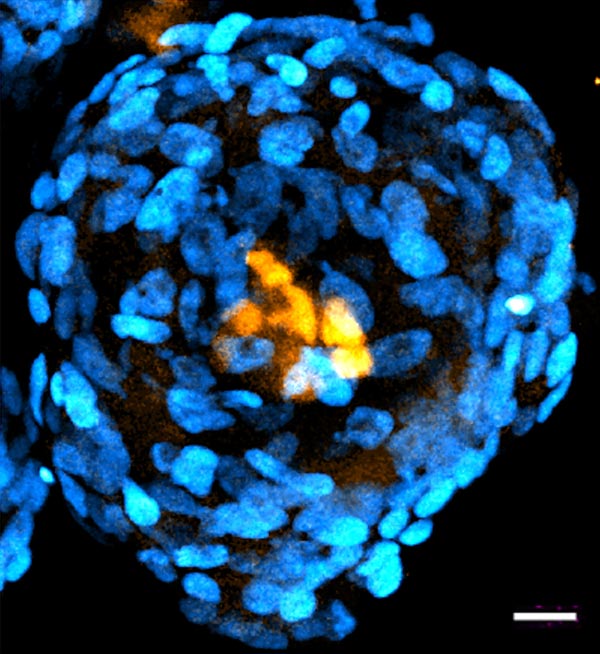
Structure generated entirely from human stem cells that closely mimics morphology of the human embryo.
Credit: Sozen & Jorgensen et al., Nature Communications (2021)
The technique is an alternative to using donated embryos resulting from IVF.
Research on human embryos is vital to understanding the earliest stages of human development. Currently, this research is conducted on surplus embryos willingly donated by individuals who have undergone in vitro fertilization. Nevertheless, this research is limited by the availability of embryos and strict international ethical time limits on how long an embryo is allowed to develop in the laboratory (14 days maximum).
Now, Caltech researchers have created embryo-like structures out of human stem cells. In contrast to natural embryos that are formed by a combination of sperm and egg, these structures are formed by combining so-called pluripotent stem cells, which have the ability to develop into specialized types of cells. Though these embryo-like structures have some key differences from real embryos, the technology to create them will be critical in answering open questions about human development without the need for donated embryos.
The research was conducted in the laboratory of Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz, Bren Professor of Biology and Biological Engineering at Caltech, and is described in a paper appearing in the journal Nature Communications on September 21.
The structures are made from a type of pluripotent stem cell that gives rise to distinct types of cells that then self-assemble into a structure with morphology clearly reminiscent of that of an embryo, which has distinct embryonic and extra-embryonic tissues. The pluripotent stem cells were initially isolated from a real human embryo by other researchers and have since been maintained in a laboratory environment. Remarkably, the cells can still “remember” how to assemble into an embryo when supported by the right environmental conditions.
“The ability to assemble the basic structure of the embryo seems to be a built-in property of these earliest embryonic cells that they are simply unable to ‘forget,'” says Zernicka-Goetz. “Nevertheless, either their memory is not absolutely precise or we don’t yet have the best method of helping the cells recover their memories. We still have further work to do before we can get human stem cells to achieve the developmental accuracy that is possible with their equivalent mouse stem cell counterparts.”
The ability to generate embryo-like structures from stem cells means that additional donated embryos are not needed; in addition, the structures can be created in large quantities. Thus, this model system may lead to breakthroughs in the understanding of early embryonic development that are not constrained by the limited availability of human embryos. For example, it will be possible to perturb particular genes and study the resulting impact on the developmental process. Additionally, this system can be used to understand how different cellular components coordinate their development at very early stages and the impact of this cellular cross-talk upon later developmental stages.
The paper is titled “Reconstructing aspects of human embryogenesis with pluripotent stem cells.” Former Caltech postdoctoral scholar Berna Sozen, now at Yale University, and Caltech graduate student Victoria Jorgensen are the study’s first authors. In addition to Zernicka-Goetz, additional co-authors are Bailey Weatherbee and Meng Zhu, both members of Zernicka-Goetz’s former laboratory at the University of Cambridge, and Caltech senior research scientist Sisi Chen. Funding was provided by the Wellcome Trust, the Open Philanthropy/Silicon Valley Community Foundation, the Weston Havens Foundation, and the Shurl and Kay Curci Foundation. Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz is an affiliated faculty member with the Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute for Neuroscience at Caltech.
Journal: Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25853-4
Article Title: Reconstructing aspects of human embryogenesis with pluripotent stem cells.
Article Publication Date: 21-Sep-2021
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



