researchers evaluate mass spectrometry approaches for mold identification
The sensitivity and accuracy of three MALDI-TOF MS approaches for the identification of filamentous fungi was determined by researchers from Chung-Ang University.
Credit: Prof. Mi-Kyung Lee from Chung-Ang University
This study compares the efficacy of three mass spectrometry instruments and sample preparation techniques for the clinical diagnosis of mold.
In recent years, filamentous fungi or molds have emerged as causative agents underlying life-threatening infections in immunocompromised individuals. The timely management of these infections requires the rapid and accurate diagnosis of mold in clinical settings.
Unfortunately, traditional methods are time consuming, given the long incubation periods required to culture and examine molds. On the other hand, advanced molecular techniques are more sensitive and efficient. One such technique that can detect filamentous fungal isolates with high-sensitivity and reproducibility, is “matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS)”. It can differentiate between samples based on variations in mass and charge. However, it is not widely used due to limitations in database availability and a lack of standardized procedures.
Recently, a team of researchers from Chung-Ang University, Republic of Korea led by Professor Mi-Kyung Lee, evaluated three different MALDI-TOF MS approaches used in domestic clinical settings, for the identification of molds.
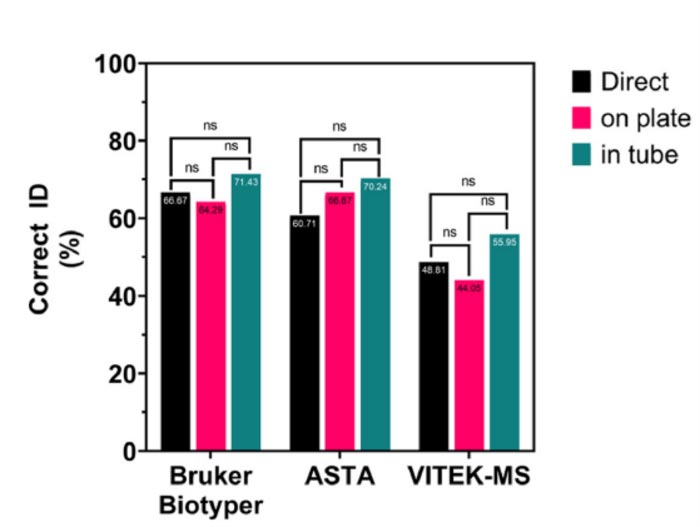
In their study published in The Journal of Clinical Microbiology on October 26, 2022, they compared the performance and diagnostic accuracy of the Bruker Biotyper, ASTA MicroIDSys, and Vitek MS. They also assessed the sensitivity of three pretreatment methods— “direct”, “on plate”, and “in tube”—using 84 filamentous fungal isolates.
Explaining the rationale behind their study, Prof. Lee remarks, “Selecting an appropriate sample preparation method can improve the efficiency and accuracy of mold identification. Additionally, the development of systemized processes at the diagnostic level can ultimately contribute to effective treatments for patients”
The study found that the Bruker Biotyper identified 71.43% of isolates correctly up to the species or genus level, while ASTA MicroIDSys and Vitek MS demonstrated accuracy rates of 70.24% and 55.95%, respectively. Furthermore, the direct method for sample preparation was favorable over the other two methods, owing to its simplicity and ease of application. Notably, identification sensitivity did not differ significantly across different sample preparation methods.
The rate of misidentification is an important consideration in clinical laboratories because it can lead to inappropriate treatment interventions for patients. In this study, only one isolate was misidentified using Vitek-MS with the on-plate method. Moreover, the species level identification of Aspergillus (a highly prevalent and clinically significant microorganism) was highest through Vitek-MS, indicating the applicability of this technique in clinical settings.
The number of incorrectly identified species were 17, 15, and 23 through the Bruker Biotyper, ASTA MicroIDSys, and Vitek MS, respectively. The team suggested the need for additional evaluations if misidentification occurred due to the absence of certain species in the library rather than an error. Furthermore, the team determined that any differences in sensitivity could be attributed to differences in the system databases.
In summary, MALDI-TOF MS is a valuable technique that can accurately identify clinically significant microorganisms in a timely manner. Process standardization and guidelines that can be applied to a wide range of species can help reduce the process bias occurring through these techniques. Additionally, limitations related to acquisition parameters, matrix quality, and hardware require further assessments.
When asked about the applications of the study, Prof. Lee says, “Our study is the first to compare the sensitivity and accuracy of three MALDI-TOF MS instruments as well as the efficacy of three pretreatment methods for filamentous fungal identification. Accurate results obtained through a simple and streamlined process for mold identification using MALDI-TOF MS could improve laboratory work efficiency for users and treatment efficiency for patients.”
Reference
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.00812-22
Authors: Yoojeong Choia, Daewon Kimb, Kye Won Choea, Hyukmin Leec, Jae-Seok Kimd, Jeong-Yeal Ahnb, and Mi-Kyung Leea
Affiliations:
aDepartment of Laboratory Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
bDepartment of Laboratory Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Republic of Korea
cDepartment of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
dDepartment of Laboratory Medicine, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
About Chung-Ang University
Chung-Ang University is a private comprehensive research university located in Seoul, South Korea. It was started as a kindergarten in 1916 and attained university status in 1953. It is fully accredited by the Ministry of Education of Korea. Chung-Ang University conducts research activities under the slogan of “Justice and Truth.” Its new vision for completing 100 years is “The Global Creative Leader.” Chung-Ang University offers undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral programs, which encompass a law school, management program, and medical school; it has 16 undergraduate and graduate schools each. Chung-Ang University’s culture and arts programs are considered the best in Korea.
Website: https://neweng.cau.ac.kr/index.do
About Professor Mi-Kyung Lee from Chung-Ang University
Dr. Mi-Kyung Lee is a professor at the Department of Laboratory Medicine at Chung-Ang University College of Medicine. She holds a PhD in Laboratory Medicine and has over 230 publications to her credit. With a research experience spanning over two decades in the fields of clinical microbiology and molecular genetics, her research is currently focused on fungal infections and antifungal drug susceptibility. With the support of the Korean Science and Engineering Foundation, she has successfully completed a 1-year training fellowship in the Mycotic Disease Branch, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, Georgia, USA in 2002, following which she consistently conducts epidemiological and molecular studies of clinical microorganisms (particularly the Candida species) in South Korea.
Journal: Journal of Clinical Microbiology
DOI: 10.1128/jcm.00812-22
Method of Research: Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: Performance Evaluation of Bruker Biotyper, ASTA MicroIDSys, and VITEK-MS and Three Extraction Methods for Filamentous Fungal Identification in Clinical Laboratories
Article Publication Date: 26-Oct-2022
COI Statement: None
Media Contact
Se-Jin Oh
Chung-Ang University
shinn0015@cau.ac.kr
Office: 02-820-6614
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Parallel Paths: Understanding Malaria Resistance in Chimpanzees and Humans
The closest relatives of humans adapt genetically to habitats and infections Survival of the Fittest: Genetic Adaptations Uncovered in Chimpanzees Görlitz, 10.01.2025. Chimpanzees have genetic adaptations that help them survive…

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…



