Revolutionize genomic sequencing
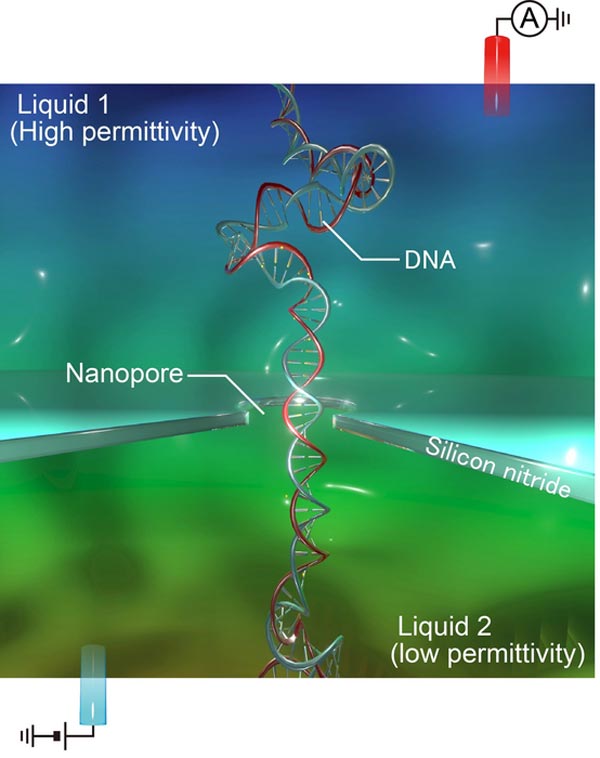
Liquid permittivity gradient-mediated ionic current measurements for enhanced sensitivity of nanopore DNA sensors.
Credit: Makusu Tsutsui
… will silicon nitride and common chemistry help?
A research group led by Osaka University found a simple way to facilitate detections of single DNA molecules in silicon nitride nanopores, integration of which with compact electronics will be straightforward and could revolutionize genomic sequencing.
Genomic sequencing has revolutionized our understanding of medicine and evolution, such as identifying hereditary anomalies. Arrays of nanometer-sized holes—nanopores—in silicon nitride can in principle dramatically speed up and lower the cost of such analyses. However, DNA molecules transit such nanopores far too quickly for detection causing only weak signals that are often difficult to analyze. Now, a research study led by The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research (SANKEN) at Osaka University has utilized a method to enhance DNA detection in nanopores by manipulating the electrical properties of the DNA within and slowing down its transit.
The direct compatibility of silicon nitride with compact electronics has long attracted researchers at the interface of biology and technology. However, the use of corresponding nanopores for DNA sequencing has faced bottlenecks that are difficult to overcome. “DNA usually moves through the nanopores too fast, and the instrumental response is too weak, to read the genome sequence,” explains Makusu Tsutsui, lead author. “Our research could change this. Simply using glycerol, instead of water, on one side of the nanopores enables detection of single DNA molecules.”
The researchers’ nanopore-based DNA detection strategy monitors the change in electrical current upon transit of a DNA molecule through the nanopore. Water is commonly used on both sides of the nanopore. By using glycerol on one side, the flow of solvent through the nanopore substantially changes. The way in which this altered flow of solvent modifies the ion flow through the nanopore increases the intensity of the instrument’s readout so that DNA molecules can be detected.
“The difference in viscosity between the two ends of the nanopore is what makes everything work,” says Tomoji Kawai, senior author. “The altered fluid flow through the channel changes the electrical response of the DNA within the channel, and sufficiently slows down DNA transit for further enhanced instrumental detection.
“One limitation of this method is that fast current fluctuations add substantial noise to the instrumental readout. The researchers noted that mathematical tools such as wavelet transforms could be used to address this, because these tools are ideal for analyzing transiently fluctuating DNA electrical response data.
The detection of DNA molecules may also facilitate genomic sequencing, which provides a comprehensive readout of the DNA composition. Perhaps with such capabilities, researchers will be able to integrate solid-state nanopores with compact electronics for unprecedented functionality, such as identifying the real-time onset of hereditary anomalies.
The article, “Ionic signal amplification of DNA in a nanopore,” was published in Small Methods at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202200761
Journal: Small Methods
DOI: 10.1002/smtd.202200761
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: Ionic signal amplification of DNA in a nanopore
Article Publication Date: 5-Oct-2022
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
Osaka University
gi-strategy@cgin.osaka-u.ac.jp
Office: 81-661-055-886
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Hyperspectral imaging lidar system achieves remote plastic identification
New technology could remotely identify various types of plastics, offering a valuable tool for future monitoring and analysis of oceanic plastic pollution. Researchers have developed a new hyperspectral Raman imaging…

SwRI awarded $26 million to develop NOAA magnetometers
SW-MAG data will help NOAA predict, mitigate the effects of space weather. NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) recently awarded Southwest Research Institute a $26 million contract…

Protein that helps cancer cells dodge CAR T cell therapy
Discovery could lead to new treatments for blood cancer patients currently facing limited options. Scientists at City of Hope®, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment…



