Scientists improve a photosynthetic enzyme by adding fluorophores
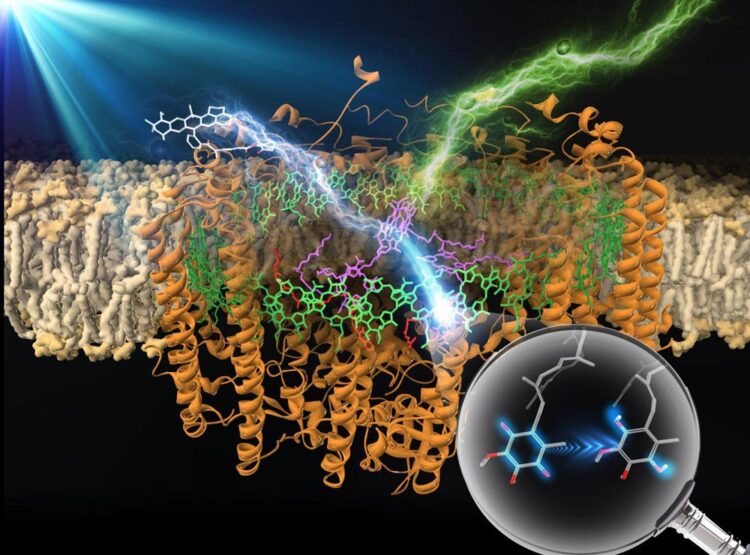
Broadening the enzyme's band of harvestable light wavelengths is an important improvement given the extremely low energy density of sunlight.
Image credit: Takehisa Dewa from Nagoya Institute of Technology
In new study, scientists show how covalently linking fluorophores to the enzyme broadens the range of wavelengths convertible into chemical energy.
Given the finite nature of fossil fuel reserves and the devastating environmental impacts of relying on fossil fuels, the development of clean energy sources is among the most pressing challenges facing modern industrial civilization. Solar energy is an attractive clean energy option, but the widescale implementation of solar energy technologies will depend on the development of efficient ways of converting light energy into chemical energy.
Like many other research groups, the members of Professor Takehisa Dewa’s research team at Nagoya Institute of Technology in Japan have turned to biological photosynthetic apparatuses, which are, in Prof. Dewa’s words, both “a source of inspiration and a target to test ways of improving the efficiency of artificial systems.” Specifically, they chose to focus on the purple photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris, which uses a biohybrid light-harvesting 1-reaction center core complex (LH1-RC) to both capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy.
In their initial studies of R. palustris, Prof. Dewa’s group quickly noted that the LH1-RC system has certain limitations, such as only being able to harvest light energy efficiently within a relatively narrow wavelength band due to its reliance on (bacterio)chlorophylls, a single light-harvesting organic pigment assembly (B875, named for its absorption maximum). To overcome this limitation, the researchers, in partnership with collaborators at Osaka University and Ritsumeikan University, experimented with covalently linking the LH1-RC system to a set of fluorophores (Alexa647, Alexa680, Alexa750, and ATTO647N). The results of their experiments appear in a paper published in a recent issue of the Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology A: Chemistry.
Having synthesized their modified LH1-RC system, Prof. Dewa’s team used a method called “femtosecond transient absorption spectroscopy” to confirm the presence of ultrafast “excitation energy” transfer from the fluorophores to the bacteriochlorophyll a pigments in the B875 assembly. They also confirmed the subsequent occurrence of “charge separation” reactions, a key step in energy harvesting. Unsurprisingly, the rate of excitation energy transfer increased with greater spectral overlap between the emission bands of the fluorophores and the absorption band of B875. Attaching the external light-harvesting fluorophores boosted the enzyme’s maximum yield of charge separation and photocurrent generation activity on an electrode within an artificial lipid bilayer system.
By introducing covalently linked fluorophores into a bacterial photosynthetic enzyme (as shown in Figure 1), Prof. Dewa’s team succeeded in broadening the enzyme’s band of harvestable light wavelengths. This is an important improvement given the extremely low energy density of sunlight. “This finding could pave the way to developing an efficient artificial photosynthesis system for solar energy conversion,” notes Prof. Dewa. “Research on biohybrids should provide insights into the development of implementable energy conversion systems, thereby giving advanced modern civilization a practical option for accessing an inexhaustible supply of clean solar energy,” he adds.
The energy conversion systems in question may take many forms, including various nanomaterials, such as quantum dots and nanocarbon materials, but a unifying feature will be the need for some way to harness a broad-spectrum light-harvesting apparatus to a photocurrent-generating apparatus, and the biohybrid-type system developed by Prof. Dewa’s team provides a feasible means of addressing this need.
###
About Nagoya Institute of Technology, Japan
Nagoya Institute of Technology (NITech) is a respected engineering institute located in Nagoya, Japan. Established in 1949, the university aims to create a better society by providing global education and conducting cutting-edge research in various fields of science and technology. To this end, NITech provides a nurturing environment for students, teachers, and academicians to help them convert scientific skills into practical applications. Having recently established new departments and the “Creative Engineering Program,” a 6-year integrated undergraduate and graduate course, NITech strives to continually grow as a university. With a mission to “conduct education and research with pride and sincerity, in order to contribute to society,” NITech actively undertakes a wide range of research from basic to applied science.
About Professor Takehisa Dewa from NITech
Takehisa Dewa, D.Eng., is a Professor at the Department of Life Science and Applied Chemistry at Nagoya Institute of Technology (NITech), Japan. He completed his postgraduate education at Osaka Prefecture University and the Tokyo Institute of Technology, and he completed postdoctoral fellowships at Lehigh University and Kyushu University. He became an Assistant Professor at NITech in 2001, and he became a full Professor in 2016. His research interests include biomolecular assemblies, photosynthetic antenna systems, and synthetic drug delivery systems. He has published about 100 research papers in prestigious journals.
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Parallel Paths: Understanding Malaria Resistance in Chimpanzees and Humans
The closest relatives of humans adapt genetically to habitats and infections Survival of the Fittest: Genetic Adaptations Uncovered in Chimpanzees Görlitz, 10.01.2025. Chimpanzees have genetic adaptations that help them survive…

You are What You Eat—Stanford Study Links Fiber to Anti-Cancer Gene Modulation
The Fiber Gap: A Growing Concern in American Diets Fiber is well known to be an important part of a healthy diet, yet less than 10% of Americans eat the minimum recommended…

Trust Your Gut—RNA-Protein Discovery for Better Immunity
HIRI researchers uncover control mechanisms of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) and the Julius-Maximilians-Universität (JMU) in Würzburg have identified a…



