Seeing protein crystals in a different light
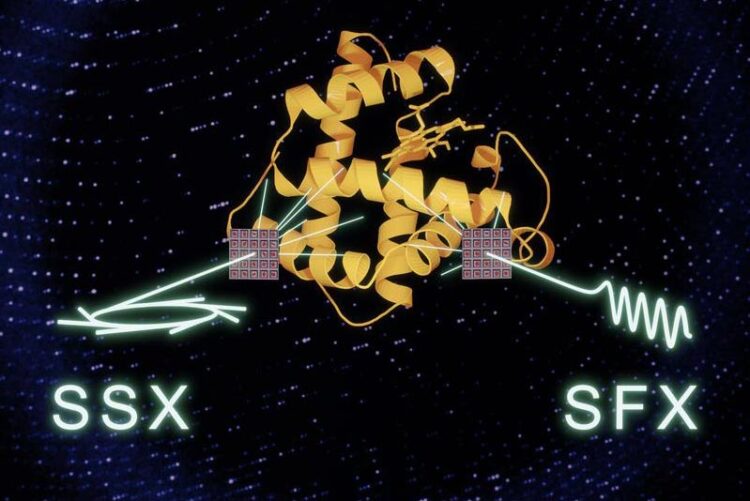
Ein systematischer Vergleich zeigt, dass Synchrotrons und XFELs Daten von gleichwertiger Qualität erzeugen. Dies eröffnet neue Wege für kollaborative Anwendungen, um beide Strahlungsquellen für die Erforschung der biomolekularen Dynamik zu nutzen
Jörg Harms / MPSD
An international team of researchers from the MPSD (Max Planck institute for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter) at the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science in Hamburg, the University of Toronto (Canada), the Diamond Light Source in Oxford (UK) and the EMBL (European Molecular Biology Laboratory) Hamburg has found that two of the worlds brightest light sources offer more common research possibilities than originally anticipated. Although they operate on very different timescales, synchrotrons and XFELs can produce data of equivalent quality as long as serial data collection is used in the imaging process. The team’s work has been published in Science Advances.
All life is dynamic and so are its molecular building blocks. The motions and structural changes of biomolecules are fundamental to their function. However, understanding these dynamic motions at a molecular level is a formidable challenge. For decades, researchers have relied on X-rays provided by more than fifty synchrotron light sources around the world and made use of protein crystals to understand the molecular architecture of the building blocks of life.
In recent years, researchers designed a new generation of X-ray light sources to comprehend even the fastest motions in proteins: X-ray free electron lasers (XFEL). Uniquely, these ultrabright light sources can capture snapshots of protein dynamics within fractions of a trillionth of a second. However, their light pulses destroy the protein crystals and therefore several thousand have to be examined to obtain a complete structure – in contrast to canonical structure determination at synchrotrons using only a single crystal. Hence at XFELs each crystal is exposed only once to the X-ray beam and rapidly replaced by a new one. This process is called serial data collection.
To understand how a structure changes as the protein carries out its work, a reaction is initiated in the crystals which are subsequently exposed to the extremely bright XFEL pulses at defined delay times. These snapshots can then be assembled into a series of pictures which provide insights into the dynamics underlying even the fastest processes of life, from the fixation of carbon-dioxide to the water-splitting reaction during photosynthesis or the processes involved in human vision. Unfortunately, there are currently only seven XFELs operational around the world, which limits general access and restricts their use to specialized groups.
However, the majority of protein reactions is completed in about a tenth of a second, just the blink of an eye – but a snail’s pace compared to the ultrafast examples given above and well within the reach of widely accessible synchrotrons, which can routinely provide insights into processes that are up to a thousand times faster than that.
But if the timescales are so different are the results really comparable? The team’s work shows that they are – as long as serial data collection and crystals of similar size are used in the imaging process at both types of light sources. At XFELs, the technique is crucial because the samples are destroyed by their exposure to the X-rays. But as this study shows, the use of serial data collection also minimizes radiation damage at synchrotrons and produces results of an equivalent quality.
This is an important result, as it allows scientists to address comprehensive questions by combining the key strengths of both light sources. In other words: the fastest dynamics can be addressed at highly specialized XFELs while slower dynamics can be tackled at more broadly available synchrotrons.
The combination of both light sources should therefore broaden the scope of biomolecular dynamics. This would also facilitate further detailed research into the workings of health-related proteins, including those playing key roles in infectious diseases like SARS-CoV2 or pathogenic bacteria resistant to antibiotic therapy. Ultimately, these fundamental new insights will enable scientists to develop better future treatments for a wide range of conditions.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Pedram Mehrabi, lead author: pedram.mehrabi@mpsd.mpg.de
Originalpublikation:
https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/7/12/eabf1380
Weitere Informationen:
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

An Endless Loop: How Some Bacteria Evolve Along With the Seasons
The longest natural metagenome time series ever collected, with microbes, reveals a startling evolutionary pattern on repeat. A Microbial “Groundhog Year” in Lake Mendota Like Bill Murray in the movie…

Witness Groundbreaking Research on Achilles Tendon Recovery
Achilles tendon injuries are common but challenging to monitor during recovery due to the limitations of current imaging techniques. Researchers, led by Associate Professor Zeng Nan from the International Graduate…

Why Prevention Is Better Than Cure—A Novel Approach to Infectious Disease Outbreaks
Researchers have come up with a new way to identify more infectious variants of viruses or bacteria that start spreading in humans – including those causing flu, COVID, whooping cough…



