
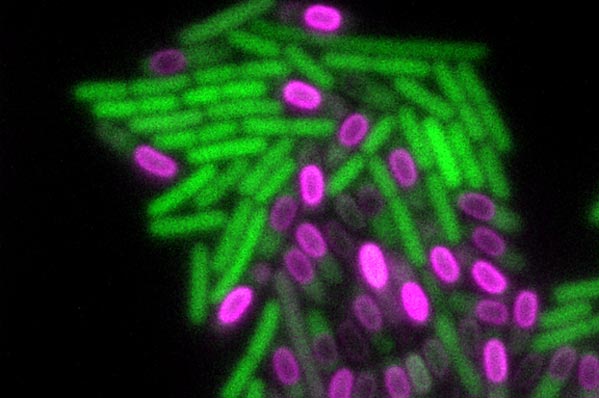
Image depicts a B. subtilis biofilm transitioning between stressed cells (green) and cells differentiating into dormant spores (magenta).
Credit: Kwang-Tao Chou
Genetic mechanism found that enables communities of bacterial cells to organize into surprisingly sophisticated segments, revealing a similarity to how plants and animals develop.
Over the past several years, research from University of California San Diego biologist Gürol Süel’s laboratory has uncovered a series of remarkable features exhibited by clusters of bacteria that live together in communities known as biofilms.
Biofilms are prevalent in the living world, inhabiting sewer pipes, kitchen counters and even the surface of our teeth. A previous research study demonstrated that these biofilms employ sophisticated systems to communicate with one another, while another proved biofilms have a robust capacity for memory.
Süel’s laboratory, along with researchers at Stanford University and the Universitat Pompeu Fabra in Spain, has now found a feature of biofilms that reveal these communities as far more advanced than previously believed. Biological Sciences graduate student Kwang-Tao Chou, former Biological Sciences graduate student Daisy Lee, Süel and their colleagues discovered that biofilm cells are organized in elaborate patterns, a feature that previously only had been associated with higher-level organisms such as plants and animals. The findings, which describe the culmination of eight years of research, are published Jan. 6 in the journal Cell.
“We are seeing that biofilms are much more sophisticated than we thought,” said Süel, a UC San Diego professor in the Division of Biological Sciences’ Section of Molecular Biology, with affiliations in the San Diego Center for Systems Biology, BioCircuits Institute and Center for Microbiome Innovation. “From a biological perspective our results suggest that the concept of cell patterning during development is far more ancient than previously thought. Apparently, the ability of cells to segment themselves in space and time did not just emerge with plants and vertebrates, but may go back over a billion years.”
Biofilm communities are made up of cells of different types. Scientists previously had not thought that these disparate cells could be organized into regulated complex patterns. For the new study, the scientists developed experiments and a mathematical model that revealed the genetic basis for a “clock and wavefront” mechanism, previously only seen in highly evolved organisms ranging from plants to fruit flies to humans. As the biofilm expands and consumes nutrients, a “wave” of nutrient depletion moves across cells within the bacterial community and freezes a molecular clock inside each cell at a specific time and position, creating an intricate composite pattern of repeating segments of distinct cell types.
The breakthrough for the researchers was the ability to identify the genetic circuit underlying the biofilm’s ability to generate the biofilm community-wide concentric rings of gene expression patterns. The researchers were then able to model predictions showing that biofilms could inherently generate many segments.
“Our discovery demonstrates that bacterial biofilms employ a developmental patterning mechanism hitherto believed to be exclusive to vertebrates and plant systems,” the authors note in the Cell paper.
The study’s findings offer implications for a multitude of research areas. Because biofilms are pervasive in our lives, they are of interest in applications ranging from medicine to the food industry and even the military. Biofilms as systems with the capability to test how simple cell systems can organize themselves into complex patterns could be useful in developmental biology to investigate specific aspects of the clock and waveform mechanism that functions in vertebrates, as one example.
“We can see that bacterial communities are not just globs of cells,” said Süel, who envisions research collaborations offering bacteria as new paradigms for studying developmental patterns. “Having a bacterial system allows us to provide some answers that are difficult to obtain in vertebrate and plant systems because bacteria offer more experimentally accessible systems that could provide new insights for the field of development.”
Coauthors of the paper include: Kwang-Tao Chou (UC San Diego graduate student), Dong-yeon Lee (former UC San Diego graduate student, now a postdoctoral scholar at Stanford University), Jian-geng Chiou (UC San Diego postdoctoral scholar), Leticia Galera-Laporta (UC San Diego postdoctoral scholar), San Ly (former UC San Diego researcher), Jordi Garcia-Ojalvo (Universitat Pompeu Fabra Professor) and Gürol Süel (UC San Diego Professor).
Journal: Cell
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.001
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Cells
Article Title: A segmentation clock patterns cellular differentiation in a bacterial biofilm
Article Publication Date: 6-Jan-2022
Media Contact
Mario Aguilera
University of California – San Diego
maguilera@ucsd.edu
Office: 858-822-5148












