Stepping toward a smaller carbon footprint
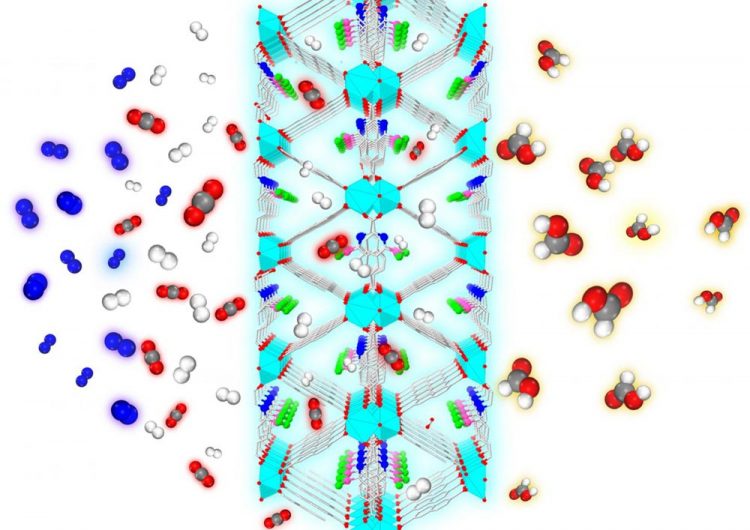
From the left, a mixture of gases, including CO2 (red and gray), N2 (blue), and H2 (white) are exposed to the nanoporous metal-organic framework designed by the Johnson group. Only the CO2 and H2 enter the MOF, which rejects the N2. The catalytic sites within the framework convert the CO2 to formic acid (red, gray and white), a chemical precursor to methanol Credit: Swanson School of Engineering/Johnson Group
Burning fossil fuels such as coal and natural gas releases carbon into the atmosphere as CO2 while the production of methanol and other valuable fuels and chemicals requires a supply of carbon. There is currently no economically or energy efficient way to collect CO2 from the atmosphere and use it to produce carbon-based chemicals, but researchers at the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering have just taken an important step in that direction.
The team worked with a class of nanomaterials called metal-organic frameworks or “MOFs,” which can be used to take carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere and combine it with hydrogen atoms to convert it into valuable chemicals and fuels. Karl Johnson, the William Kepler Whiteford Professor in the Swanson School's Department of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering, led the research group as principal investigator.
“Our ultimate goal is to find a low-energy, low-cost MOF capable of separating carbon dioxide from a mixture of gases and prepare it to react with hydrogen,” says Dr. Johnson. “We found a MOF that could bend the CO2 molecules slightly, taking them to a state in which they react with hydrogen more easily.”
The Johnson Research Group published their findings in the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) journal Catalysis Science & Technology (DOI: 10.1039/c8cy01018h). The journal featured their work on its cover, illustrating the process of carbon dioxide and hydrogen molecules entering the MOF and exiting as CH2O2 or formic acid–a chemical precursor to methanol. For this process to occur, the molecules must overcome a demanding energy threshold called the hydrogenation barrier.
Dr. Johnson explains, “The hydrogenation barrier is the energy needed to add two H atoms to CO2, which transforms the molecules into formic acid. In other words, it is the energy needed to get the H atoms and the CO2 molecules together so that they can form the new compound. In our previous work we have been able to activate H2 by splitting two H atoms, but we have not been able to activate CO2 until now.”
The key to reducing the hydrogenation barrier was to identify a MOF capable of pre-activating carbon dioxide. Pre-activation is basically preparing the molecules for the chemical reaction by putting it into the right geometry, the right position, or the right electronic state.
The MOF they modeled in their work achieves pre-activation of CO2 by putting it into a slightly bent geometry that is able to accept the incoming hydrogen atoms with a lower barrier.
Another key feature of this new MOF is that it selectively reacts with hydrogen molecules over carbon dioxide, so that the active sites are not blocked by CO2.
“We designed a MOF that has limited space around its binding sites so that there is not quite enough room to bind CO2, but there is still plenty of room to bind H2, because it is so much smaller. Our design ensures that the CO2 does not bind to the MOF but instead is free to react with the H molecules already inside the framework,” says Dr. Johnson.
Dr. Johnson believes perfecting a single material that can both capture and convert CO2 would be economically viable and would reduce the net amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
“You could capture CO2 from flue gas at power plants or directly from the atmosphere,” he says. “This research narrows our search for a very rare material with the ability to turn a hypothetical technology into a real benefit to the world.”
###
The Pitt Center for Research Computing contributed computing resources.
About the Johnson Research Group
The Johnson Research Group at the University of Pittsburgh uses atomistic modeling to tackle fundamental problems over a wide range of subject areas in chemical engineering, including the molecular design of nanoporous sorbents for the capture of carbon dioxide, the development of catalysts for conversion of carbon dioxide into fuels, the transport of gases and liquids through carbon nanotube membranes, the study of chemical reaction mechanisms, the development of CO2-soluble polymers and CO2 thickeners, and the study of hydrogen storage with complex hydrides.
About Dr. Johnson
Karl Johnson is an Associate Director of the Center for Research Computing and a member of the Pittsburgh Quantum Institute. He received his B.S. and M.S. in chemical engineering from Brigham Young University, and PhD in chemical engineering with a minor in computer science from Cornell University.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

ASXL1 Mutation: The Hidden Trigger Behind Blood Cancers and Inflammation
Scientists show how a mutated gene harms red and white blood cells. LA JOLLA, CA—Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have discovered how a mutated gene kicks off…

Recharging the Future: Batteries Built for Extreme Cold Using Negative Thermal Expansion
Most solids expand as temperatures increase and shrink as they cool. Some materials do the opposite, expanding in the cold. Lithium titanium phosphate is one such substance and could provide…

Self-Destructing Cancer Cells: Cutting-Edge RNA Breakthrough
Jülich scientists use novel RNA technology to selectively switch off tumours in the brain. An Adaptable Platform Technology That Destroys Glioblastoma Cancer Cells Using a special RNA molecule, a team…



