Strong evidence – Essential regulatory gene for the formation of heart valves discovered
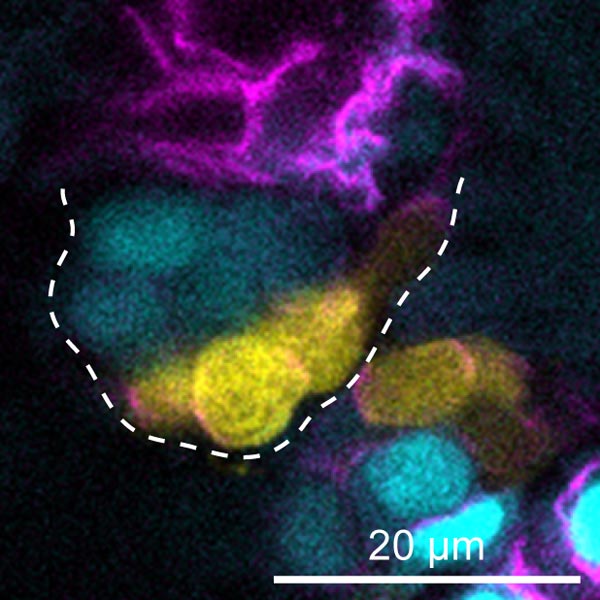
Im embryonalen Herzen vom Zebrafisch ist die Herzinnenwand, welche die Herzklappen bildet, in zwei Populationen unterteilt (hier: cyan und gelb). Bildrechte: Federica Fontana
During embryonic development, the heart is the first organ that becomes functional and generates blood flow throughout the body.
The special thing about its morphogenesis is the interconnection with the biomechanical forces due to blood flow.
These forces have a big impact in particular on the cells that line the interior of the heart. From these cells, cardiac valves are formed to ensure an unidirectional flow of blood.
Zebrafish eggs can easily be manipulated and are therefore a widely used model system in biomedical research. Taking advantage of the zebrafish embryo, the researchers around Salim Seyfried combined in vivo imaging and gene expression profiling – the measurement of the activity of thousands of genes at once – to visualize the conversion of genetic information into proteins (gene expression) under conditions with and without blood flow, respectively.
They observed higher Vegfr3/Flt4 gene expression in endocardial cells that lost contact to blood flow after they migrated into the area between the endocardium and the myocardium.
By studying zebrafish embryos that are defective for the Vegfr3/Flt4 gene, the team found that Vegfr3/Flt4 is essential for the proper formation of cardiac valves. Federica Fontana, first author of the paper now published, explains:
„In particular, our work suggests that valve endocardial cells in the area between the endocardium and the myocardium loose expression of another gene (Notch), due to the lack of mechanical stimuli, and this triggers gene expression of Vegfr3/Flt4. In turn, Vegfr3/Flt4 suppresses the Notch-gene in these cells.” These activities represent a fine-tuned gene regulatory mechanism, essential to shape cardiac valve leaflets by inducing unique differences in the fates of endocardial cells.
Link to Publication: Federica Fontana, Timm Haack, Maria Reichenbach, Petra Knaus, Michel Puceat, Salim Abdelilah-Seyfried, 2020, Antagonistic Activities of Vegfr3/Flt4 and Notch1b Fine-tune Mechanosensitive Signaling during Zebrafish Cardiac Valvulogenesis, Cell Reports 32, 107883, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107883
Image: In the embryonic zebrafish heart, the endocardium that is forming cardiac valve leaflets is divided into two subpopulations (here, cyan and yellow). Yellow cells are in contact with blood flow and express Notch, while Vegfr3/Flt4 is active within the cyan cells that lack blood flow stimuli. Their antagonistic activities shape the cardiac valves. Image Credit: Federica Fontana
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Salim Seyfried, Institute of Biochemistry and Biology, Tel.: +49 331 977-5540, salim.seyfried@uni-potsdam.de
Federica Fontana, Institute of Biochemistry and Biology, Tel.: +49 331 977-5539, fontanat@uni-potsdam.de
Media Information 03-08-2020 / Nr. 075
Dr. Stefanie Mikulla
Universität Potsdam
Referat Presse- und Öffentlichkeitsarbeit
Am Neuen Palais 10
14469 Potsdam
Tel.: +49 331 977-1474
Fax: +49 331 977-1130
E-Mail: presse@uni-potsdam.de
Internet: www.uni-potsdam.de/presse
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

An Endless Loop: How Some Bacteria Evolve Along With the Seasons
The longest natural metagenome time series ever collected, with microbes, reveals a startling evolutionary pattern on repeat. A Microbial “Groundhog Year” in Lake Mendota Like Bill Murray in the movie…

Witness Groundbreaking Research on Achilles Tendon Recovery
Achilles tendon injuries are common but challenging to monitor during recovery due to the limitations of current imaging techniques. Researchers, led by Associate Professor Zeng Nan from the International Graduate…

Why Prevention Is Better Than Cure—A Novel Approach to Infectious Disease Outbreaks
Researchers have come up with a new way to identify more infectious variants of viruses or bacteria that start spreading in humans – including those causing flu, COVID, whooping cough…



