The Bizarre Mating Habits of Flatworms
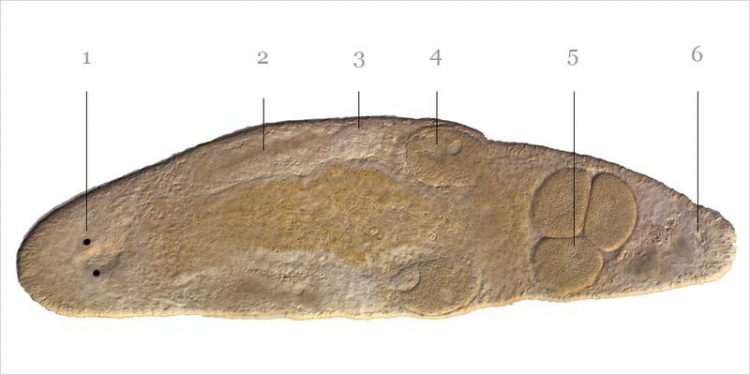
MicrMacrostomum hystrix showing the anterior eyes (1) in the head, followed by the paired testes (2), paired ovaries (3), developing eggs (4), the female genitalia containing three ma (Image: Lukas Schärer)
Zoologists from the Universities of Basel and Bielefeld have discovered the extraordinary lengths to which this animal is willing to go in order to reproduce – including apparently injecting sperm directly into their own heads. The academic journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B has published their findings.
The absence of a mate usually spells disaster for sexually reproducing animals. However, some simultaneous hermaphrodites – animals who have both male and female sex organs at the same time – have developed an escape route for this scenario: self-fertilization. It is an imperfect solution, as any offspring produced by so-called “selfing” are bound to be inbred, but still better than not reproducing at all.
In previous studies, it had been established that the flatworm species Macrostomum hystrix is capable of switching to just such selfing behavior when isolated from mating partners, a behavior found in many but not all simultaneous hermaphrodites. In their new study, Dr. Lukas Schärer from the University of Basel and his team now show the bizarre, yet remarkable mechanisms Macrostomum hystrix has developed that make this possible.
A shot to the head
The studied flatworms are highly transparent and their insides can therefore be easily observed under the microscope. By doing so, the zoologists discovered that under selfing conditions, when hermaphroditic individuals had to use their own sperm to fertilize their own eggs, the worms had very few sperm in their tail region.
This is in stark contrast to worms kept in a group, which contained most sperm in their tails, close to where fertilization actually occurs. Instead, isolated worms had more sperm in their head region.
This implies a rather strange insemination route: by using its needle-like male copulatory organ, an isolated worm can self-inject sperm into its own anterior body, from where the sperm then moves through the body towards the eggs.
“As far as we know, this is the first described example of hypodermic self-injection of sperm into the head. To us this sounds traumatic, but to these flatworms it may be their best bet if they cannot find a mate but still want to reproduce” explains Dr. Steven Ramm, first-author of the study.
Such a convoluted route is likely needed because, although hermaphrodites, there are no internal connections between the worm’s male and female reproductive systems.
Original source
Ramm SA, Schlatter A, Poirier M, Schärer L (2015)
Hypodermic Self-Insemination as a Reproductive Assurance Strategy
Proceedings of the Royal Society B | doi:10.1098/rspb.2015.0660
Further information
Lukas Schärer, University of Basel, Zoological Institute, Tel. +41 61 267 03 66, email: lukas.scharer@unibas.ch
Steven A. Ramm, Evolutionary Biology, Bielefeld University, Tel. +49 521 106 2719, email: steven.ramm@uni-bielefeld.de
https://www.unibas.ch/en/News-Events/News/Uni-Research/The-Bizarre-Mating-Habits…
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



