The viruses in our genes
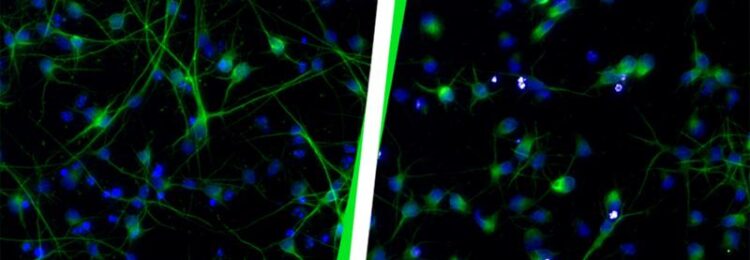
Neurons on the right have lost their function and show a different phenotype.
Credit: Helmholtz Zentrum München / Michelle Vincendeau
When activated, they damage brain development …
Since our ancestors infected themselves with retroviruses millions of years ago, we have carried elements of these viruses in our genes – known as human endogenous retroviruses, or HERVs for short. These viral elements have lost their ability to replicate and infect during evolution, but are an integral part of our genetic makeup. In fact, humans possess five times more HERVs in non-coding parts than coding genes. So far, strong focus has been devoted to the correlation of HERVs and the onset or progression of diseases. This is why HERV expression has been studied in samples of pathological origin. Although important, these studies do not provide conclusions about whether HERVs are the cause or the consequence of such disease.
Today, new technologies enable scientists to receive a deeper insight into the mechanisms of HERVs and their function. Together with her colleagues, virologist Michelle Vincendeau* has now succeeded for the first time in demonstrating the negative effects of HERV activation on human brain development.
HERV activation impairs brain development
Using CRISPR technology, the researchers activated a specific group of human endogenous retroviruses** in human embryonic stem cells and generated nerve cells (neurons). These viral elements in turn activated specific genes, including classical developmental factors, involved in brain development. As a result, cortical neurons, meaning the nerve cells in our cerebral cortex, lost their function entirely. They developed very differently from healthy neurons in this brain region – with much a shorter axon (nerve cell extension) that were much less branched. Thus, activation of one specific HERV group impairs cortical neuron development and ultimately brain development.
Clinical relevance
Since neurodegenerative diseases are often associated with the activation of several HERV groups, the negative impact of HERV activation on cortical neuron development is an essential finding. It is already known that environmental factors such as viruses, bacteria, and UV light can activate distinct HERVs, thereby potentially contributing to disease onset. This knowledge, in turn, makes HERVs even more interesting for clinical application. Switching off distinct viral elements could open up a new field of research for the treatment of patients with neurodegenerative diseases. In a next step, the group at Helmholtz Zentrum München will study the impact of HERV deactivation in neurons in the context of disease.
New paths for basic research
In addition, the research findings provide important indications that epigenetic mechanisms keep viral elements under control in healthy brain development. Michelle Vincendeau even suspects a functional role for the controlled HERVs in normal brain development. “We have carried these elements for about 40 to 70 million years. We assume that their presence is relevant to our natural processes, otherwise we would not have retained them for so long during evolution,” Vincendeau says. Further basic research in this direction might reveal new functional roles for HERVs.
###
* Michelle Vincendeau leads the research group for Human Endogenous Retroviruses at the Institute of Viorology at Helmholtz Zentrum München. Part of the data from the current study was generated in the context of her previous work at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York. For this paper, she also collaborated with researchers at the Technical University of Munich and the University of Saarland.
** HERV-K(HML-2)
Original publication
Nair et al., 2021: Activation of HERV-K(HML-2) disrupts cortical patterning and neuronal differentiation by increasing NTRK3. Cell Stem Cell, DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.04.009
Helmholtz Zentrum München
Helmholtz Zentrum München is a research center with the mission to discover personalized medical solutions for the prevention and therapy of environmentally-induced diseases and promote a healthier society in a rapidly changing world. It investigates important common diseases which develop from the interaction of lifestyle, environmental factors and personal genetic background, focusing particularly on diabetes mellitus, allergies and chronic lung diseases. Helmholtz Zentrum München is headquartered in Neuherberg in the north of Munich and has about 2,500 staff members. It is a member of the Helmholtz Association, the largest scientific organization in Germany with more than 40,000 employees at 18 research centers.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



