UCSB researchers find a way to detect stealthy, 'hypervirulent' Salmonella strains
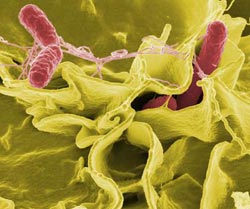
Salmonella typhimurium (red) invades cultured human cells in this color-enhanced scanning electron micrograph. Credit: Rocky Mountain Laboratories, NIAID, NIH<br>
Their findings, in a paper titled “Intraspecies Variation in the Emergence of Hyperinfectious Bacterial Strains in Nature,” have been published in the journal PLoS Pathogens.
Salmonella is the most common cause of infection, hospitalization, and death due to foodborne illness in the U.S. This burden may continue to worsen due to the emergence of new strains that would tax current health-control efforts. To address this problem, researchers sought out –– and found –– hypervirulent strains that present a potential risk to food safety and the livestock industry.
An international team of scientists –– which also included Robert Sinsheimer and William Shimp from UCSB; Yi Xie and Bart Weimer from UC Davis; and John House from University of Sydney, Australia –– conducted a global search for hypervirulent Salmonella strains. They were found among isolates derived from livestock, and rendered current vaccines obsolete.
Bacteria behave like a Trojan Horse, exposing their weapons only after initiating infection. “These strains exhibit this behavior in the extreme –– essentially having a '5th gear' they can switch to during infection,” said Heithoff, lead author of the paper.
Previous efforts to find hypervirulent strains were unsuccessful since bacteria behave much like their less-virulent cousins after environmental exposure. “The trick was to assess their virulence during infection –– before they switch back to a less-virulent state in the lab,” said Professor Mahan.
Now that researchers know what to look for, they are developing methods to rapidly detect and discriminate the more harmful strains from their less-virulent cousins. The strategy is aided by a special medium utilized by the researchers that forces the bacteria to reveal their weapons in the laboratory –– the first step in the design of therapeutics to combat them.
Humans usually get Salmonella food poisoning from eating contaminated beef, chicken, or eggs. However, animal waste can contaminate fields where fruits, nuts, and vegetables are grown, thus posing a particular health concern for vegetarians. The threat is exacerbated when these foods are not cooked. Salmonella control efforts are expensive –– recent estimates place this cost up to $14.6 billion annually in the U.S.
As hypervirulent strains pose a potential risk to human and animal health, mitigation efforts warrant researchers' careful attention. “Now that we have identified the problem –– and potential solutions –– we just need to get to work,” Heithoff said.
This research was launched with support from The G. Harold & Leila Y. Mathers Foundation, which then leveraged additional funding from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, National Institutes of Health, U.S. Army, and Santa Barbara Cottage Hospital Research Program.
To read the paper, visit: http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002647
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.ucsb.eduAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Decoding Cancer: 40 Years of Breakthroughs in Genetic Research
Cancer in children and adolescents is rare. Nevertheless, malignant diseases are still one of the most common causes of death in this age group. Survivors of childhood or adolescent cancer…

Let’s Think Before the First Drink: How Early Substance Use Might Lead to Brain Structure Differences Among Adolescents
Many differences appeared to exist prior to any substance use, pointing to the role brain structure may play in substance use risk, NIH-supported study suggests. Studies reveal factors that expose…

Combating Kidney Cancer Using Enhanced Immunotherapies
Medical University of South Carolina Hollings Cancer Center researcher receives Department of Defense Early Career Scholar Award to improve immune therapies by targeting resistant kidney tumors. A Medical University of…



