Watching Molecular Machines at Work
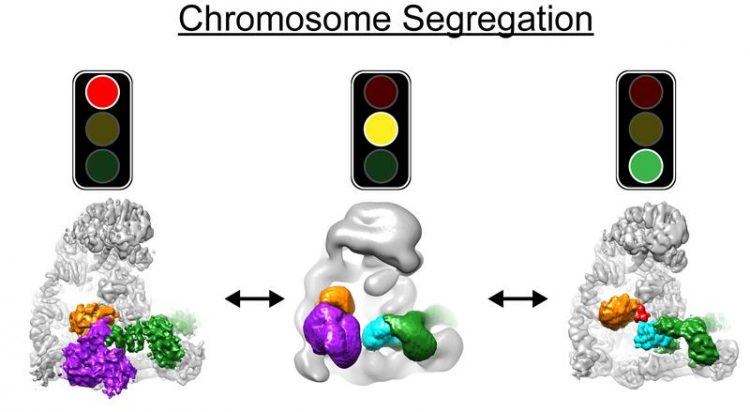
Cryo EM structures of APC/C in three states: Left, off, before cells are ready for chromosome segregation; Middle, in the process of turning on; Right, on, in action, to turn on cell division. Masaya Yamaguchi and Nicholas Brown, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital
When one cell divides into two – that is how all forms of life are propagated – the newly born daughter cells have to be equipped with everything they will need in their tiny lives. Most important of all is that they inherit a complete copy of the genetic information from their mother cell.
If this is not the case because a wrong number of chromosomes – on which the genetic information is stored – gets passed on during cell division, the daughter cells will often not survive, or worse, contribute to the development of diseases such as cancer or conditions such as Down Syndrome. Segregating chromosomes correctly is therefore of great importance and cells use complex molecules to carry out this process.
How one of these “molecular machines” works has now been elucidated by Jan-Michael Peters from the Research Institute of Molecular Pathology (IMP) in Vienna, Holger Stark from the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry in Göttingen and Brenda Schulman from St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in Memphis. They describe their findings in a series of four papers that have been published this year in PNAS, Cell and Molecular Cell.
Unprecedented resolution reveals molecular details
Like humans, cells use machines to carry out the complicated tasks they are confronted with, such as chromosome segregation. These molecular machines are often as elaborate as man-made devices, but exactly how they work is much harder to understand because of their extremely small size. While an engineer could study a man-made machine relatively easily or take it apart to figure out how it works, a molecular machine is typically only a ten thousandth of a millimetre in size. That has made it incredibly difficult for scientists to understand how these molecules work.
“If one could actually look at molecular machines, it would be much easier to understand how they work”, explains IMP-director Jan-Michael Peters. Exactly that has now become possible with new techniques for generating synthetic forms of these molecular machines. The new technology, developed recently at the IMP, makes it possible to test how these complex molecules function by manipulating them systematically.
Add to this a new electron microscopy technique that brings resolution down to the atomic level – and indeed scientists are now able to directly look at these machines. For this purpose, they are first frozen at very low temperatures and then analysed with electron beams that can be measured with new detectors of unprecedented precision. With these approaches, machines built of tiny protein molecules can now be visualised, even though they are less than a hundredth of a human hair in diameter.
Molecular complex switches itself on
The teams of Brenda Schulman, Holger Stark and Jan-Michael Peters have applied these approaches to visualise a molecular machine called the APC/C. “APC/C initiates chromosome segregation and it does this only after the mother cell has completed all other steps that are necessary for cell division. We knew all of this, because otherwise daughter cells with the wrong chromosome numbers would be born – with catastrophic consequences”, explains Jan-Michael Peters, “But we did not know how the APC/C is switched on at the right time”.
The work of Brenda Schulman, Holger Stark and Jan-Michael Peters has now directly visualised the APC/C machine before and after it is switched on. “Interestingly, this revealed that the APC/C can switch itself on, like a smart hybrid car knows when to switch from the electric to the gas engine or vice versa”, says Brenda Schulman.
“Without directly being able to see the APC/C in detail by electron microscopy, we would have never been able to find out”, adds Holger Stark. “In the future, the new technology will allow us to visualise and understand molecular processes at a level we could so far only dream of.” In the long run, the scientists hope that their work will help to understand how errors in chromosome segregation and the diseases and syndromes caused by them can be prevented.
Original Publications
Mechanism of APC/CCDC20 activation by mitotic phosphorylation. Renping Qiao et al. PNAS, 2016 May 10;113(19): E2570-8. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1604929113
biGBac—Rapid gene assembly for expression of large multisubunit protein complexes. Florian Weissmann et al. PNAS, 2016 May 10; 113(19): E2564-9. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1604935113
Dual RING E3 Architectures Regulate Multiubiquitination and Ubiquitin Chain Elongation by APC/C. Nicholas G. Brown et al. Cell 165, 1440–1453, June 2, 2016. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.037
Cryo EM of Mitotic Checkpoint Complex-bound APC/C reveals reciprocal and conformational regulation of ubiquitin ligation. Masaya Yamaguchi et al. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.07.003
Media Contact at the IMP
Dr. Heidemarie Hurtl
IMP Communications
Research Institute of Molecular Pathology
Dr. Bohr-Gasse 7
A 1030 Vienna
+43 (0)1 79730 3625
hurtl@imp.ac.at
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Innovative vortex beam technology
…unleashes ultra-secure, high-capacity data transmission. Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type…

Tiny dancers: Scientists synchronise bacterial motion
Researchers at TU Delft have discovered that E. coli bacteria can synchronise their movements, creating order in seemingly random biological systems. By trapping individual bacteria in micro-engineered circular cavities and…

Primary investigation on ram-rotor detonation engine
Detonation is a supersonic combustion wave, characterized by a shock wave driven by the energy release from closely coupled chemical reactions. It is a typical form of pressure gain combustion,…



