Four-legged robotic system that can walk a balance beam
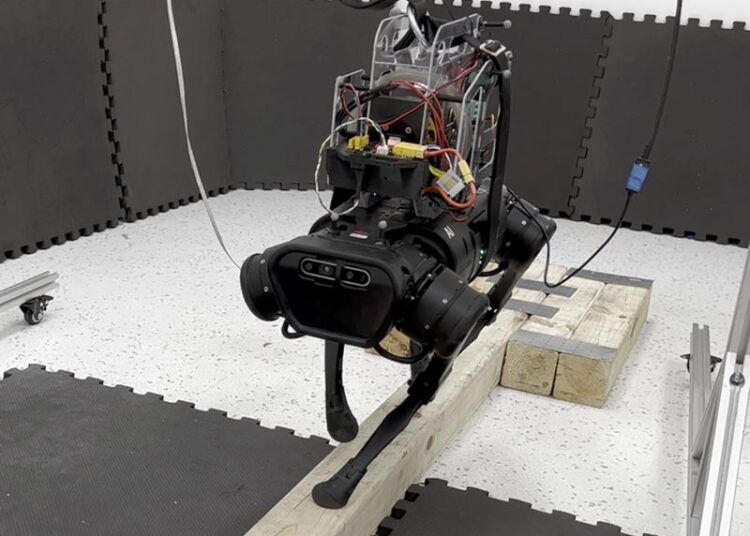
A Carnegie Mellon University team designed a four-legged robotic system that can walk a balance beam, a likely first.
Credit: Carnegie Mellon University
Spacecraft-inspired system enhances quadruped agility and balance.
Researchers in Carnegie Mellon University’s Robotics Institute (RI) have designed a system that makes an off-the-shelf quadruped robot nimble enough to walk a narrow balance beam — a feat that is likely the first of its kind.
“This experiment was huge,” said Zachary Manchester, an assistant professor in the RI and head of the Robotic Exploration Lab. “I don’t think anyone has ever successfully done balance beam walking with a robot before.”
By leveraging hardware often used to control satellites in space, Manchester and his team offset existing constraints in the quadruped’s design to improve its balancing capabilities.
The standard elements of most modern quadruped robots include a torso and four legs that each end in a rounded foot, allowing the robot to traverse basic, flat surfaces and even climb stairs. Their design resembles a four-legged animal, but unlike cheetahs who can use their tails to control sharp turns or falling cats that adjust their orientation in mid-air with the help of their flexible spines, quadruped robots do not have such instinctive agility. As long as three of the robot’s feet remain in contact with the ground, it can avoid tipping over. But if only one or two feet are on the ground, the robot can’t easily correct for disturbances and has a much higher risk of falling. This lack of balance makes walking over rough terrain particularly difficult.
“With current control methods, a quadruped robot’s body and legs are decoupled and don’t speak to one another to coordinate their movements,” Manchester said. “So how can we improve their balance?”
The team’s solution employs a reaction wheel actuator (RWA) system that mounts to the back of a quadruped robot. With the help of a novel control technique, the RWA allows the robot to balance independent of the positions of its feet.
RWAs are widely used in the aerospace industry to perform attitude control on satellites by manipulating the angular momentum of the spacecraft.
“You basically have a big flywheel with a motor attached,” said Manchester, who worked on the project with RI graduate student Chi-Yen Lee and mechanical engineering graduate students Shuo Yang and Benjamin Boksor. “If you spin the heavy flywheel one way, it makes the satellite spin the other way. Now take that and put it on the body of a quadruped robot.”
The team prototyped their approach by mounting two RWAs on a commercial Unitree A1 robot — one on the pitch axis and one on the roll axis — to provide control over the robot’s angular momentum. With the RWA, it doesn’t matter if the robot’s legs are in contact with the ground or not because the RWAs provide independent control of the body’s orientation.
Manchester said it was easy to modify an existing control framework to account for the RWAs because the hardware doesn’t change the robot’s mass distribution, nor does it have the joint limitations of a tail or spine. Without needing to account for such constraints, the hardware can be modeled like a gyrostat (an idealized model of a spacecraft) and integrated into a standard model-predictive control algorithm.
The team tested their system with a series of successful experiments that demonstrated the robot’s enhanced ability to recover from sudden impacts. In simulation, they mimicked the classic falling-cat problem by dropping the robot upside down from nearly half a meter, with the RWAs enabling the robot to reorient itself mid-air and land on its feet. On hardware, they showed the robot’s ability to recover from disturbances — as well as the system’s balancing capability — with an experiment where the robot walked along a 6-centimeter-wide balance beam.
Manchester predicts that quadruped robots will soon transition from being primarily research platforms in labs to widely available commercial-use products, similar to where drones were about 10 years ago. And with continued work to enhance a quadruped robot’s stabilizing capabilities to match the instinctual four-legged animals that inspired their design, they could be used in high-stakes scenarios like search-and-rescue in the future.
“Quadrupeds are the next big thing in robots,” Manchester said. “I think you’re going to see a lot more of them in the wild in the next few years.”
To the team’s knowledge, this is the first instance of a quadruped successfully walking on a narrow balance beam. Their paper, “Enhanced Balance for Legged Robots Using Reaction Wheels,” was accepted to the 2023 International Conference on Robotics and Automation. The annual conference will be held May 29–June 2, in London.
Media Contact
Aaron Aupperlee
Carnegie Mellon University
aaupperlee@cmu.edu
Office: 412-268-9068
Original Source
All latest news from the category: Machine Engineering
Machine engineering is one of Germany’s key industries. The importance of this segment has led to the creation of new university degree programs in fields such as production and logistics, process engineering, vehicle/automotive engineering, production engineering and aerospace engineering among others.
innovations-report offers informative reports and articles covering technologies such as automation, motion, power train, energy, conveyor, plastics, lightweight construction, logistics/warehousing, measurement systems, machine tools and control engineering.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



