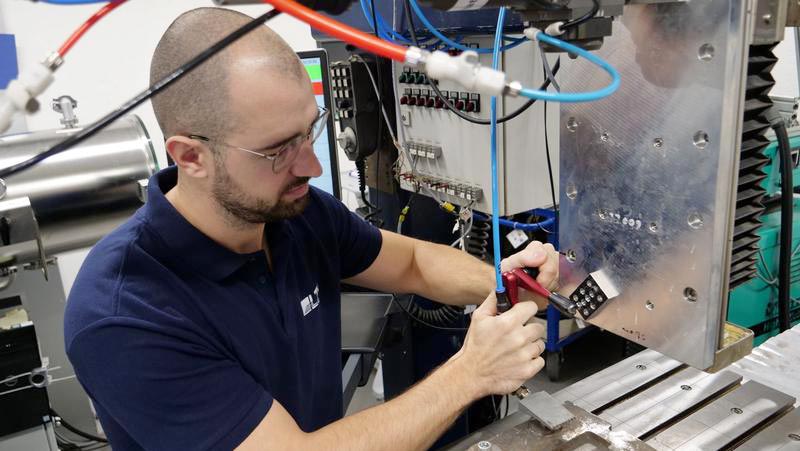


The LZH is researching a controlled laser beam welding process for brass
Photo: LZH
Brass is used for many components, but welding the copper alloy is challenging. The Laser Zentrum Hannover e.V. (LZH) wants to change this together with LMB Automation GmbH, Iserlohn. In the project LaserMessing, they are developing a laser-based manufacturing system for automated production of brass components such as fittings, bearings, valves, turbines or heat exchangers.
Within the project LaserMessing, the scientists of the LZH are working on a welding process that combines laser-based deep welding and cored wire processes. The goal: a stable, automatable process with weld seams free of pores, weld spatters and underfill – for components with high aesthetic demands.
Controlled process for high weld seam quality
For this, the scientists of the group Joining and Cutting of Metals rely on a controllable method in combination with adaptable beam profiles, which unites two processes. They will use thermography and spectroscopy data to monitor the process and develop a process control system together with LMB. In doing so, they aim to target energy into the workpieces and reduce vapor capillary fluctuations. The process is to be additionally stabilized by the use of core and ring spots. The subsequent laser cored wire process smooths the seam surface of the previously created deep welds for applications in the field of vision.
Laser beam welding of brass: A challenge
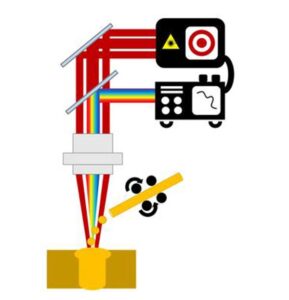
Draft: LZH
The processing of the copper alloy brass is challenging, but laser beam welding is in principle well suited for its processing. Laser beam welding places only a low thermal load on the workpiece and achieves very narrow and deep seams. It is also very easy to automate, fast and precise. However, processes specifically for joining brass alloys are often still affected by process instabilities. The alloyed zinc already evaporates below the melting temperature of copper. For this reason, pore formation and a high hot cracking tendency of the seams occur.
Brass has a very good electrical conductivity and high corrosion resistance, as well as an attractive appearance. For this reason, brass components are used in many applications ranging from fittings, machinery, and apparatus engineering to power plants, vehicles, and shipbuilding. An automated welding solution will enable LMB Automation GmbH to offer its customers welding processes for the series production of brass components and thus decisively expand its product portfolio.
About LaserMessing
Partners of the project LaserMessing („Entwicklung einer Fertigungsstrategie zum prozesssicheren Laserstrahlschweißen von Messingbauteilen“) are the Laser Zentrum Hannover e.V. and the LMB Automation GmbH, Iserlohn. The project ist funded by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (grant agreement no.KK5111708KX1).














